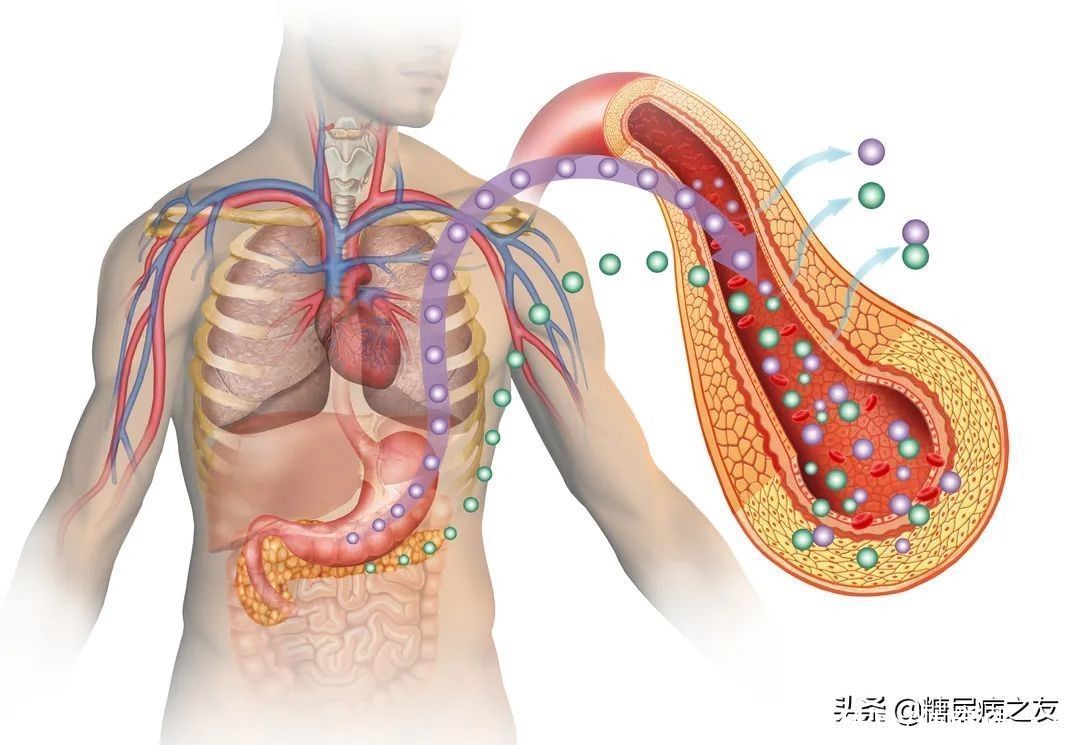
Among the many blood glucose testing indicators, the indicator that can predict the risk of diabetes complications is glycated hemoglobin, abbreviated as
Glycation is the product of the encounter and combination of glucose in blood and hemoglobin in red blood cells. The test sheet shows HbA1c in English, which can reflect the average blood sugar level in the last 2-3 months.
The relationship between high glycated hemoglobin and diabetic complications
The normal value of glycated hemoglobin is 4%-6%. If the long-term control of glycated hemoglobin is unstable, it will change the affinity of red blood cells for oxygen, and cause:
- Increase in blood lipids and blood viscosity, and accelerate cardiovascular and cerebrovascular complications
- thickening of the glomerular basement membrane, which induces diabetic nephropathy;
- the lens of the eye is saccharified, may cause cataracts.
Therefore, the level of glycated hemoglobin is closely related to the complications of diabetes. A 1% reduction in glycated hemoglobin significantly reduces the risk of diabetes-related complications.
The meaning of different glycated hemoglobin values
1. When the glycated hemoglobin is between 4% and 6%: means that the blood sugar is under normal control.
2. When the glycated hemoglobin is between 6% and 7%: means ideal blood sugar control.
3. When the glycated hemoglobin is between 7% and 8%: means that the blood sugar is generally controlled.
4. When the glycated hemoglobin is at 8%~9%: means the control is not ideal.
5. When glycated hemoglobin >9%: means poor blood sugar control, which is the development of chronic complications Risk factors may lead to complications such as diabetic nephropathy, arteriosclerosis, cataract, and acute complications such as ketoacidosis.
Teach you 6 tips to stay away from diabetes complications
1. The diet should be reasonable
The type and quantity of carbohydrates in each meal should be reasonable to prevent excessive intake of carbohydrates or excessive calories High blood sugar levels lead to increased postprandial blood sugar;
Avoid excessive intake of fats, such as cooking oil, fatty meat, butter and nuts; excessive intake of fat can lead to Blood sugar rises 3 hours, 4 hours, or even longer after a meal.
Timed meals: 4-6 hours between meals, and dinner before 19:00.
2. Quit smoking, limit alcohol
Quitting smoking can Reduces the risk of myocardial infarction, cerebral infarction, nerve damage and kidney damage.
Diabetes patients can drink alcohol, but it must be limited (no more than 2 times a week) and limited (no more than 25 grams of alcohol per drink for men and no more than 15 for women) gram).
Because long-term alcohol consumption in diabetic patients can cause severe increase in blood sugar, diabetes-related complications such as hypertension, atherosclerosis, cerebral infarction, cerebral arterial insufficiency, Aggravated diabetic peripheral neuropathy.

3. After dinner exercise
Exercise after dinner, such as walking, jogging, swimming, etc., can not only lower postprandial blood sugar, but also help lower fasting blood sugar the next day.
Exercise after breakfast and after lunch is okay. Start exercising 1 hour after a meal and continue for 30-40 minutes, which is very effective in lowering postprandial blood sugar.
4. Lose weight
Losing weight There are many benefits, such as lowering blood sugar, blood pressure, blood lipids, uric acid, reducing the risk of diabetes complications, improving mental state, and enhancing personal self-confidence.
5. Standardized treatment of diabetes strong>
Timely and standardized treatment is a wise choice for diabetic patients to reduce glycosylated hemoglobin.
For example, newly diagnosed diabetic patients, glycosylated hemoglobin ≥ 9.0% or fasting blood glucose ≥ 11.1% mmol/L with obvious symptoms of hyperglycemia (eating, drinking, urine, etc.) 2-3 months of short-term intensive insulin therapy.
For another example, on the basis of lifestyle intervention and oral drug intervention, blood sugar still does not reach the blood sugar control target set by the doctor, and insulin therapy needs to be started in time.
In short, you cannot see high blood sugar without taking any intervention.
6. Do annual checkups for diabetes complications
Check for diabetic complications when the body has symptoms There are no symptoms, and by the time there is fatigue, swelling, or changes in vision, the disease is already serious.
Therefore, diabetic patients should develop the habit of regularly checking the complications of diabetes, and go to the endocrinology department to ask a doctor to issue a list.
In addition, friends with diabetes also need to avoid staying up late in life, learn to decompress, follow doctor’s orders, and strive to control blood sugar, blood pressure, blood lipids, and weight to the target within the range.
If you have any questions about the prevention of diabetes complications, please leave a message. We will work together on the road to lowering diabetes. Your “like” and “watching” are the greatest help to us. Support, thanks!
Author: Fang Yu