This article is reprinted from: Guangming.com
With the arrival of summer, the “dog days” thunderstorms and high temperatures take turns. This high temperature and humid weather has undoubtedly become a “hotbed for the breeding of bacteria and pathogens.” “. The summer season is also a prone period for gastrointestinal diseases. A little attention to dietary hygiene may lead to the occurrence of gastrointestinal diseases, which seriously threatens our health. Fire commanders and fighters often live in groups, with a large number of people, high aggregation, relatively closed environment, and a higher mass infection rate.
So what gastrointestinal diseases do we need to prevent in summer?
The following two types of
high incidence are introduced. Diseases:
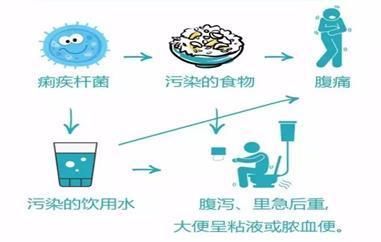
I. Bacillary dysentery
What is bacillary dysentery? Bacillary dysentery, referred to as bacillary dysentery, also known as “dirty hand disease”, is a common intestinal infectious disease caused by Shigella spp.
Typical patients usually develop symptoms within 24 to 48 hours after infection, with abdominal pain, diarrhea, accompanied by discomfort, fever, fatigue, anorexia, mucus or pus and blood in the stool, and tenesmus. Mild (atypical) patients have mild symptoms and may only have diarrhea and loose stools.
You sweat a lot after training in hot weather, and firefighters tend to lose water and salt in their bodies. Don’t be greedy at this time. In addition to the hyperactivity of gastrointestinal motility caused by cold drinks, it is mainly because the impurities and pathogenic microorganisms contained in cold water exceed the standard, which can easily cause gastrointestinal weakness and aggravate diarrhea.
What are the transmission routes of bacillary dysentery?
Food-type transmission
Bacillus dysentery can survive in vegetables, fruits and pickles for 1 to 2 weeks, so eating cold food and unclean fruits and vegetables can cause bacillary dysentery; Cooks with bacteria on their hands and cold dishes made with Shigella-contaminated food can often cause bacillary dysentery outbreaks. Cold dishes are more likely to cause food poisoning than hot dishes. If firefighters are trained in high temperature and high intensity in summer, the stomach becomes weak. , and eating cold dishes that have been placed in a high temperature environment for a long time will cause diarrhea, vomiting and other symptoms; eating leftovers that are improperly stored or deteriorated can also easily cause bacillary dysentery.
Waterborne transmission
Natural water, well water, and tap water contaminated with feces are often the source of bacillary dysentery outbreaks. When firefighters carry out activities such as training and security in the wild, it is difficult to ensure clean water sources, and they should not directly drink water sources with pollution risks.

Do not drink unclean water directly
Daily contact transmission
Mainly through contaminated hands Spread, such as tables and chairs, training equipment, doorknobs, bus handrails, etc. If you grab the food with the contaminated hand immediately, it will send the bacteria into the mouth and cause disease.
Transmission by flies
Flies have the habit of eating both feces and food, which can easily cause food contamination and are an important medium for the spread of bacillary dysentery.
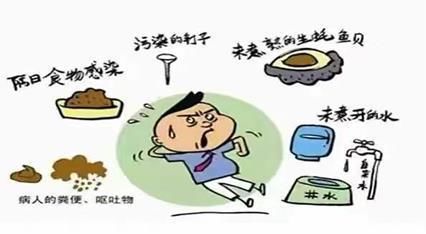
How to prevent bacillary dysentery?
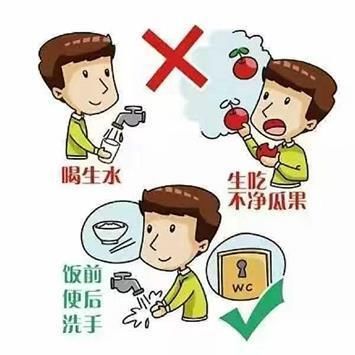
Pay attention to tableware hygiene
The kitchen must be cleaned up, the refrigerator must be cleaned frequently, and the cabinet must be kept ventilated. Maintaining proper ventilation also prevents mosquitoes from entering.
Pay attention to personal hygiene
Be sure to develop good hygiene habits and wash your hands before and after eating.
Pay attention to indoor hygiene
In summer, you must remember to install screen doors and screens indoors to reduce the entry of mosquitoes. Flies and flying insects carry a lot of bacteria. If they cannot be eliminated well, the hygiene of the diet cannot be guaranteed.
Pay attention to dietary hygiene
Whether it is fruit or vegetable, it needs to be cleaned before eating; leftovers and leftovers in the refrigerator also contain certain bacteria and must be put in the pot It is necessary to completely heat it in the refrigerator to kill the bacteria inside; the food should not be stored in the refrigerator for too long, and the fruit in the refrigerator should also be washed before eating.
Second, food poisoning
Food poisoning refers to the occurrence of food poisoning after eating food contaminated with toxic and harmful substances or containing toxic and harmful substances. Acute and subacute diseases. Patients often have symptoms such as diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, dehydration, shock, and even death due to organ failure in severe cases.
Food poisoning can be divided into bacterial food poisoning, mycotoxin poisoning, plant food poisoning, animal food poisoning, chemical food poisoning:
Bacterial food poisoning:
p>
Summer is a season of high incidence of bacterial food poisoning. Bacterial food poisoning is caused by ingesting food invaded by bacteria. Leftovers that have been left for too long, fish, shrimp, crab, shellfish, etc. in the polluted ocean; dairy products, meat products, etc. that have been kept in the refrigerator for too long.

Plant food poisoning:
such as poisonous mushrooms, sprouted potatoes, etc. Eating lentils and beans undercooked can also cause poisoning. Fire commanders and fighters must pay special attention when they want to eat wild fruits and wild fungi during outdoor training and zipper training, and only eat them after ensuring safety.

Animal food poisoning:
Accidental ingestion of puffer fish, snails, toads, etc., or high histidine content When the mackerel and other fish are stale or corrupt, a large amount of histamine is produced, which can cause poisoning after eating.
Chemical food poisoning:
Accidental ingestion of pesticide mixtureGrowing grain-processed foods, vegetables and fruits that have not been sprayed with pesticides, misuse of chemical poisons or contaminated containers for food; misuse of toxic chemicals, feed additives, etc.
What should I do if I have food poisoning?
Water: Drink plenty of clean water immediately to dilute toxins.
Induce vomiting: Press the throat with your fingers and spit out the food in the stomach as much as possible.
Storage: Store the eaten food to prevent more people from being harmed.
Call for help: immediately call the emergency center for help. The sooner you go to the hospital, the better the rescue. If it exceeds 2 hours, the poison will be absorbed into the blood, which will increase the difficulty of treatment.
How to Prevent Food Poisoning
1. Keep Clean: Wash hands and work surfaces before, during and after food preparation. Bacteria can live in many places around the kitchen, including your hands, utensils, cutting boards and countertops.
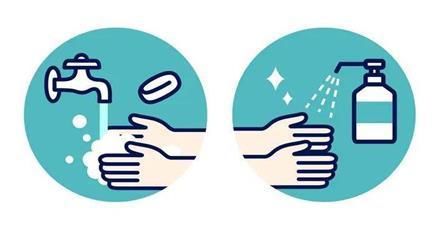
2. Separate raw and cooked: Separate raw meat, poultry, seafood and eggs from ready-to-eat food. Use a separate cutting board and keep raw meat away from other foods in your cart and refrigerator.
3. Cooking food: Cook food to the right temperature to kill harmful bacteria.
4. Keep food at a safe temperature: Keep the refrigerator at 4°C or below. Refrigerate leftovers within 2 hours of cooking.