Half a century ago, all patients with chronic kidney failure ended in death. The emergence of dialysis has brought hope to many patients with chronic kidney disease, improved the survival rate of patients with chronic kidney disease, and greatly improved chronic kidney disease. Quality of life in patients with kidney disease.
There are two main types of dialysis: one is hemodialysis and the other is peritoneal dialysis. At present, most kidney patients in my country choose hemodialysis, but in recent years, more and more kidney patients choose peritoneal dialysis.
In fact, both hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis have their own advantages and disadvantages. Today, I will introduce the advantages and disadvantages of hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis and the standardized management after dialysis.
The two dialysis methods have their own advantages
hemodialysis
Among the dialysis patients, about 68.54% of them choose hemodialysis

- can remove most of the small molecule toxins
- professionals help to complete
- No need to stock up on treatment items at home
- Short treatment time
li>

- Poor removal of medium and large molecules
- Requires special equipment
- Need to establish vascular access
peritoneal dialysis

- Good for removing medium molecular substances
- Maximum protection The patient’s residual renal function
- does not require complicated equipment and is easy to operate
- can participate in work and social activities normally

- easy Peritonitis, hernia formation
- dialysis required every day
- high hygiene requirements at home
- permanent intraperitoneal dialysis intubation required
- Significant loss of protein, about 8-9g/d
The majority of kidney patients can follow the doctor’s advice, combined with their own underlying diseases, as well as their own state and distance from home, etc., Make a good choice for yourself.
Although dialysis is good, standardized management is also essential
Chronic kidney disease is a protracted battle. Therefore, in addition to dialysis itself, kidney friends also need to actively pay attention to nutritional management, indicators Monitoring and standardizing drug use, etc.
Malnutrition
Due to the high dietary restrictions of dialysis patients, about half of existing dialysis patients are facing malnutrition risks of.
The dietary principles of kidney friends should follow the following requirements: sufficient calories, high quality and low protein, high calcium and low phosphorus, low salt and low potassium, and low fat. At the same time, pay attention to controlling water intake and supplementing an appropriate amount of vitamins , trace elements.
The specific supplementary amounts of various nutrients are shown in Figure 1. Except for slight differences in protein, sodium and fluid intake, there is basically no difference in the intake of various nutrients between hemodialysis patients and peritoneal dialysis patients. .
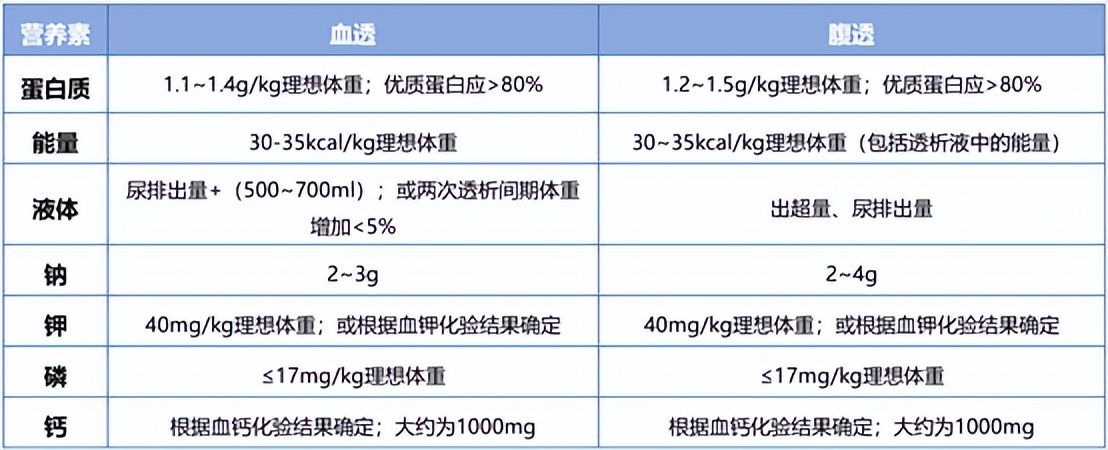
Figure 1
For kidney patients who need long-term dialysis, they also need to actively control their daily routine. Dietary phosphorus and potassium intake. The following figure (Figure 2) summarizes some common high-phosphorus and high-potassium foods for you, and you should pay special attention to them when eating them.
It’s not that kidney friends can’t eat everything, it’s just that there are some restrictions on eating, as long as they avoid eating these “blacklisted” foods, other low potassium and low sodium foods can Eat normally, don’t be afraid to eat anything because of dietary restrictions.

Figure 2
Indicator monitoring
Dry body weight is very important to maintain the quality of life of dialysis kidney patients. Too high dry body weight is prone to edema, and too low dry weight is prone to hypotension, which is not conducive to dialysis. Dry weight control is mainly reflected in three aspects:

Guaranteed that the weight gain should not exceed 1kg on weekdays and 1.5 on weekends -2kg

The formula for daily water intake is: urine volume of the previous day+(200~500)ml

It should be controlled at 3-5 g per day
In addition, dialysis kidney patients also need to ensure that the indicators of PTH, phosphorus, calcium and ALP are up to the standard, otherwise May increase risk of death. Monitoring frequency for each indicator is as follows:
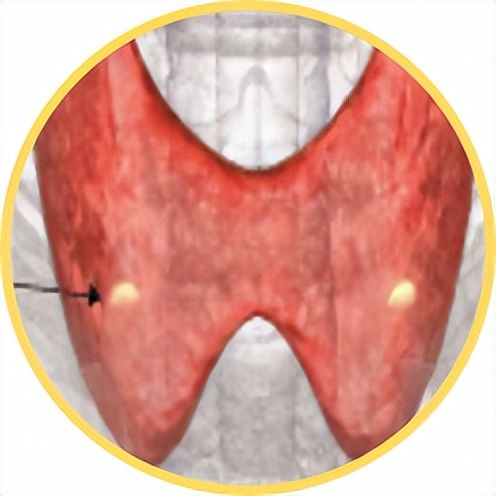
Monthly monitoring for 3 months before treatment, Once every 3 months after meeting the target

Monitor once every two weeks for 3 months before treatment, and monthly after reaching the standard 1 time

Monitor once every two weeks for 3 months before treatment and once a month after reaching the standard
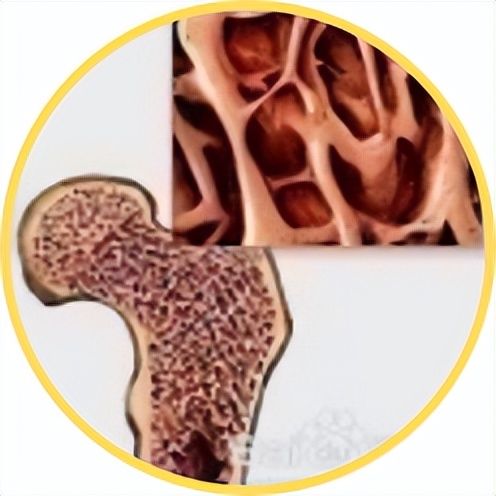
Monitor every 6-12 months
Regulated medication< /p>
Because of kidney damage, many drugs should be used with special attention, especially when using drugs marked with “use with caution in patients with liver and kidney insufficiency”, they should be used under the guidance and monitoring of doctors .
Secondary hyperparathyroidism (SHPT) is one of the common complications of long-term dialysis patients.
When using drugs to control SHPT, you should also pay attention to the following points:
- Be sure to follow the doctor’s advice and do not increase or decrease the dosage by yourself
- Apply When vitamin D receptor agonists (such as paricalcitol, etc.) inhibit the increase of PTH, it is not advisable to discontinue the drug at will. Standardized medication can effectively relieve the pain.
- Pay attention to chewing calcium tablets when applying calcium and phosphorus binders. Phosphorus binders can only be effective if they are taken with food after grinding.
In short, no matter which dialysis method is chosen, the management after dialysis needs continuous attention, especially PTH, The indicators of phosphorus, calcium and ALP, whether it is nutritional management or standardized medication, are actually closely related to these indicators.