內容目錄
“Cancer screening is a waste of money! Old Li next door has a physical examination every year. Didn’t he still find liver cancer last month?” But didn’t want to go in.
“Don’t talk about other things, I have already paid the money, it’s more than 8,000, hurry up and check it for me.”
Lao Zhang is an “old smoker” who has been smoking for more than 40 years. After learning about the neighbor’s cancer, Lao Zhang’s daughter hurriedly made an appointment for cancer screening at the local top three hospital The package, includes more than 50 items, in addition to cancer screening items, it also includes diabetes, heart disease and other items.
But in Lao Zhang’s view, this thing is the “IQ tax”, and it will cost money to cure the disease.
Cancer screening has always been a hot topic. Most hospitals offer cancer screening packages with a wide range of items and a wide price range.< span>Some people think that expensive is good, and some people think that it is just “making money”.
Han Qide, an academician of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and a pathophysiologist, delivered such a speech at the 2016 ‘Medicine and Humanities Summit Forum’: “< span>I do not advocate cancer screening for healthy people, because after early screening of cancer, the mortality rate has not actually decreased. “
Is cancer screening really necessary for ordinary people?

I. One or two cancer screenings cost at least one or two thousand yuan. Is it necessary?
Most hospitals now offer cancer screening packages. Xiaojiu checked the Internet and found that the prices of different hospitals/physical examination centers fluctuate greatly.< span>The low is one or two thousand, and the high is more than 10,000 yuan.

Tumor Screening Package of Physical Examination Center of Guangzhou Panyu District Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital (Source: Zhongkang Physical Examination Network)
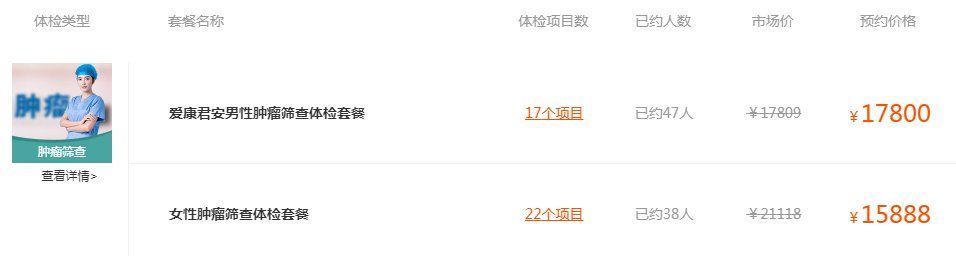
Guangzhou Aikang Junan Physical Examination Center (VVIP Department) Tumor Screening Package (Source: Zhongkang Physical Examination Network)
< /div>
The purpose of cancer screening is to let the subjects know their own cancer risk, detect precancerous lesions or early stage cancers early, and intervene at an early stage. But cancer screening does not mean that the more items and the more expensive it is, the better and more comprehensive it is.
Liu Juntian, director of the Cancer Prevention Center of Tianjin Medical University Cancer Hospitalthinks , cancer screening should be personalized, and it is not recommended for everyone to do a full set of cancer screening programs, which will not only cause economic waste, but also have chest X-rays, CT and other inspections. Injury, doing too much may cause some damage to the body.
Similarly, Academician Han Qide also thinks that it is not recommended for everyone to do universal For cancer screening, should be checked according to their own symptoms in a targeted manner. Excessive treatment can be detrimental to health.

Second, early detection of cancer may save many families hundreds of thousands of dollars
A 2020 study in the journal Cancer analyzed the financial distress of cancer patients in China.
Research points out that among cancer patients in my country, 1 in every 2 people borrows money to see a doctor, and the number of borrowers exceeds 50,000. As high as 18%, and 1 in 10 patients have to forgo some cancer treatments due to lack of money.
If early cancer screening can be done well, a large number of patients and their families can avoid this dilemma.
So early detection of cancer is important, especially in high-risk groups. The point of cancer screening is to personalize your screening, not to blindly choose packages.
3. How to do cancer screening? A one-time explanation.
Recently, the 28th National Cancer Prevention and Control Awareness Week was successfully held in Beijing. At the event, the National Cancer Center conducted screening and early diagnosis and treatment of major cancers. Methods gives the most up-to-date guidelines.
1. Esophageal cancer: endoscopy
high-risk group: over 40 years old, long-term smoker Drink alcohol, have a family history of esophageal cancer, live in an area with a high incidence of esophageal cancer, like to eat hot, pickled, and hard food, and have foreign body sensation or pain when swallowing.
Screening Recommendations:High-risk groups should undergo 1 endoscopy Check, if there is no abnormality, follow-up endoscopy is performed every 2-3 years; if there is any abnormality, follow-up endoscopy is performed once a year.
2. Gastric cancer: gastroscopy
high-risk groups : Over 40 years old, with a history of smoking, alcoholism, Helicobacter pylori infection, living in an area with a high incidence of gastric cancer, and having a family history of gastric cancer.
Screening Recommendations:Gastric cancer screening first choice for gastric cancer span>. High-risk groups are recommended to undergo a gastroscopic examination, and if there is no abnormality, a gastroscopic examination can be performed every 2-3 years; those with abnormality should undergo a subsequent gastroscopic examination every year.

3. Lung cancer: low-dose spiral CT strong>
High-risk groups: aged 40-74 years old, with a history of smoking or second-hand smoke, and a history of occupational exposure for 1 year Above, have a history of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and have a first-degree relative who has been diagnosed with lung cancer.
Screening recommendations: annual low-dose in high-risk groups Spiral CT Screening.
4. Liver cancer: serum alpha-fetoprotein detection combined with abdominal ultrasonography
High-risk groups: Males aged 45-74 years, females 50-70 years old, history of hepatitis B/C infection, history of liver cirrhosis, first- or second-degree relatives with liver cancer history.
Screening Recommendations: Serum alpha-fetoprotein preferred for high-risk individualsgroup Detection combined with abdominal ultrasonography, and then based on the comprehensive evaluation results, the diagnosis, treatment and re-examination plan were further determined.
5. Colorectal cancer: colonoscopy and fecal occult blood testing
High-risk groups: Men 40 years of age and older with a positive fecal occult blood test, a history of smoking, Overweight or obese, first-degree relatives with a family history of colorectal cancer.
Screening recommendations: High-risk groups 40-75 years old and low- and moderate-risk groups 50-74 years old should be screened for colorectal cancer. A high-quality colonoscopy every 5-10 years is recommended, in addition to an annual FIT.
6. Breast cancer: breast ultrasound
high-risk groups: Menarche before the age of 12, menopause after the age of 55, a family history of breast or ovarian cancer, a history of breast biopsy or surgery for benign breast diseases, etc.
Screening recommendations: For high-risk groups and dense breast groups, breast ultrasound combined with mammography is recommended for screening ,The general population can only do breast ultrasound examination. High-risk groups should receive annual breast cancer screening after the age of 40, and the general population aged 45-70 should receive breast cancer screening every 1-2 years.

Third, 1/3 of cancer is preventable, don’t ignore early symptoms
Qiu Meng, chief physician of the Department of Abdominal Oncology, West China Hospital, Sichuan University reminded that daily attention should be paid to physical discomfort and changes, which may be signals from cancer or precancerous diseases.
1. Unexplained weight loss
If within 6 months to 1 year , Unexplained weight loss of more than 5%, and excluding benign conditions such as insufficient energy intake, abnormal blood sugar, abnormal thyroid function, and chronic diarrhea Disease factors, need to be alert to cancer.
2. Unexplained mass on the body surface
especially Unexplained lumps appearing on the body surface of the neck, underarm, breast, groin, testis, etc.. And accompanied by poor activity, redness, pain, short-term rapid growth, and abnormal blood vessels, stains or color changes, check as soon as possible.

3. Change in bowel habits
< span>If you experience long-term constipation, diarrhea, or changes in bowel habits such as alternating constipation and diarrhea, be alert to gastrointestinal tumors occurrence of pancreatic cancer and liver cancer.
4. Persistent cough
lung cancer, breast cancer, colon cancer, kidney cancer , prostate cancer, etc., may cause persistent cough.
5. Unexplained pain
including chronic diseases, bone lesions, primary Direct or indirect compression of tumor or metastatic tumor, etc. If unexplained persistent pain occurs, especially deep pain, be sure to actively find out the cause of the pain and be alert to the occurrence of cancer.

Cancer is not a terminal illness, as long as it is detected and treated early, many cancers still have the chance to be cured. healing. Regular checkups are a good thing, but cancer screenings need to be tailored to your risk of developing cancer, or you’re wasting money and hurting your body.
Pay more attention to the changes in your body every day. Once you find any abnormal symptoms, you should go to the hospital for relevant examinations in time.
References:
[1]Is the tens of thousands of “cancer screening” worth it? A strategy for early cancer screening suitable for Chinese people. Life Times. 2019-05-22
[2] The latest release of the National Cancer Center: 6 major cancer screening methods! .Health Times.2022-04-14
[3]14 Cancer Signals You Must Know | Doctor’s Business Card.Health China.2021-12-19
Do not reprint without the author’s permission