Acute epiglottitis is one of the common critical emergencies in otorhinolaryngology, also known as supraglottic laryngitis, is a special type of epiglottis that mainly affects the supraglottic region of the larynx Acute inflammatory lesions of the surrounding tissue and epiglottis are characterized by high edema of the epiglottis.
The epiglottis is the common channel of respiration and digestion. Once the epiglottis becomes inflamed and swollen, it can cause sore throat and swallowing in mild cases, and in severe cases, it can cause difficulty in breathing, leading to suffocation and progression of the disease. Extremely fast and ferocious, it can suffocate to death in a matter of hours.
Most acute epiglottitis is caused by infection, and the most common cause is bacterial infection. It can also be caused by an infection or by a viral infection followed by a bacterial infection.
Thropharyngeal trauma, hot food, drugs or food allergies, fatigue, alcoholism, and smoking are common triggers.
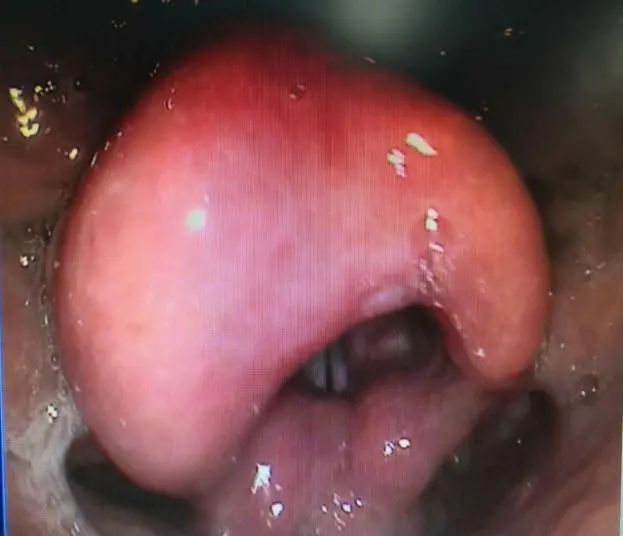
edema epiglottis
acute The typical symptom of epiglottitis is sore throat, which is the main symptom of acute infectious epiglottitis.
When the patient swallows or ingests food, it directly stimulates the epiglottis, causing aggravation of sore throat and drooling. In addition, if the surrounding tissue is swollen, swallowing may be difficult.
In severe cases, due to the highly swollen epiglottis mucosa, the entrance of the larynx is significantly reduced, and even the glottis is blocked, resulting in difficulty in breathing. As the condition worsens, suffocation may occur. Only a minority of patients presented with low, slurred speech. There may also be accompanying symptoms such as high fever, emotional agitation, whistling-like breath sounds, and slurred speech.
The disease occurs frequently throughout the year, with a high incidence in early spring and late autumn. If timely diagnosis and treatment are made, most patients have a good prognosis.
In view of the rapid onset of acute epiglottitis and the rapid progression of the disease, early detection, early diagnosis, and early treatment are extremely important to control the development of the disease. High fever, sore throat and other symptoms, accompanied by severe dysphagia, should be further examined under the guidance of a doctor. When palpitations, irritability, etc. occur, you should seek medical attention immediately to avoid delaying treatment.
Preventive measures:
The cause of acute epiglottitis is mainly bacterial or viral infection, which is related to the patient’s personal constitution, etc. more closely.
Prevention should be taken in daily life, and people should adhere to appropriate outdoor activities and participate in more sports to enhance their physical fitness.
Maintain good living habits and quit smoking and drinking.
The screening of acute epiglottitis requires patients and their families to pay attention to their own physical changes, especially in the Spring and Autumn Period, pay attention to whether there are symptoms such as sore throat, whether there are systemic symptoms such as high fever, Once it occurs, seek medical treatment in time.
Text and pictures: Zhao Junying (Otolaryngology)
Editor: Song Yuqian p>