Recently, the Thoracic Department of Shenzhen Third People’s Hospital (The Second Affiliated Hospital of Southern University of Science and Technology) treated a patient with multiple pulmonary nodules, Ms. Wang (pseudonym). During the physical examination, Ms. Wang found 4 nodules in her lungs. If they were all removed by surgery, 40% of her lung tissue would be removed, which would seriously affect her quality of life. Finally, after a multidisciplinary consultation, Ms. Wang performed thoracoscopic resection combined with microwave ablation, and the intraoperative blood loss was only 5 ml.
In 2020, Ms. Wang found nodules in her lungs during a physical examination. After several re-examinations, the nodules remained unchanged. A pulmonary nodule does not rule out the possibility of early lung cancer. After that, Ms. Wang came to the Department of Thoracic Surgery of the Third Hospital of Shenzhen City. After a multidisciplinary consultation, Qiao Kun, director of the Department of Thoracic Surgery, told Ms. Wang that her pulmonary nodules could be resolved at one time.
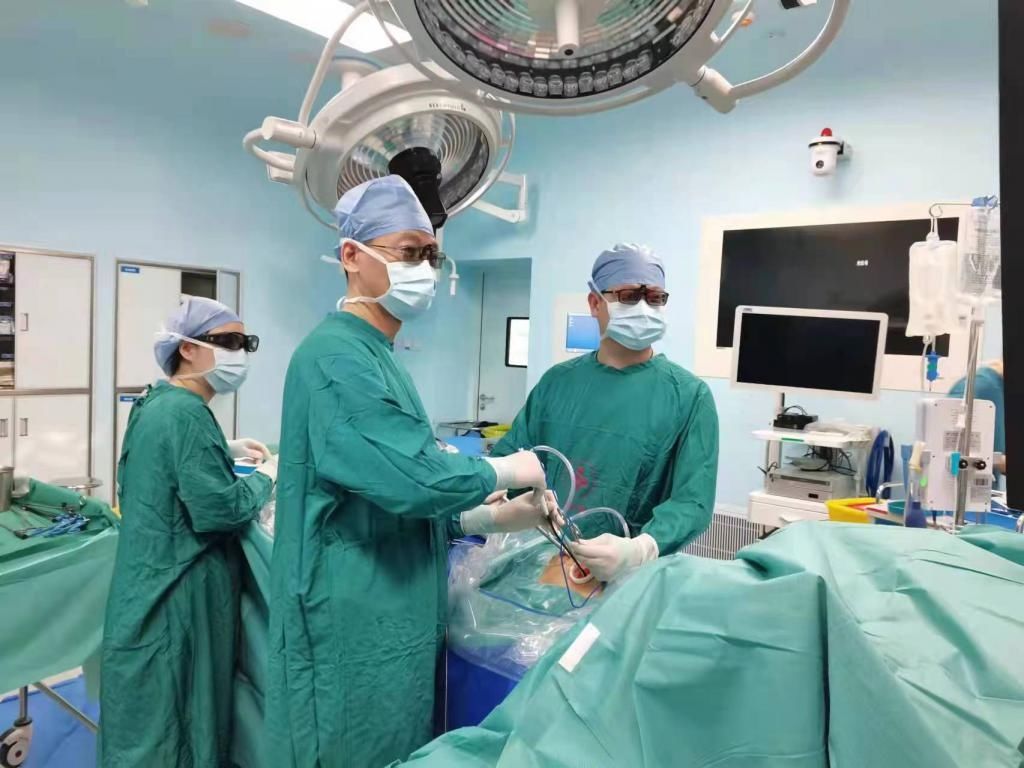
▲During surgery
Qiao Kun introduced that with the development of low-dose CT lung cancer screening With increased awareness, more and more pulmonary nodules have been found in recent years. Most of the pulmonary nodules found in the physical examination were benign nodules, and some were early lung cancers, which were mainly treated by thoracoscopic pneumonectomy. However, for patients with multiple pulmonary nodules, there are various problems with thoracoscopic surgery alone. Taking Ms. Wang as an example, the nodules in her right middle lung and right lower lung are relatively deep. If surgical resection is performed, about 40% of the lung tissue will be removed. If the nodules recur in the future, Ms. Wang will not be able to tolerate it. subject to a second operation.
In the end, Qiao Kun decided to use single-port thoracoscopy combined with CT-guided percutaneous microwave ablation to solve the problem for Ms. Wang: the right upper pulmonary nodule was removed by single-port thoracoscopic CT-guided microwave ablation of nodules located in the right middle lung and right lower lung minimized the loss of lung function.
It is reported that in 2020, Shenzhen No. 3 Hospital introduced the DISCIVERY IGS7 OR system and built a state-of-the-art hybrid operating room. The system can clearly display ground-glass nodules over five millimeters or mixed ground-glass nodules and solid nodules, and can accurately locate pulmonary nodules through special positioning methods for ablation or guided surgery. In addition, the system is also equipped with intraoperative movable vertebral beam CT, which can realize intraoperative bedside CT scanning, can plan the puncture path and angle and guide the puncture in real time, and can also improve the accuracy of puncture. Scanning to determine puncture and ablation effects.
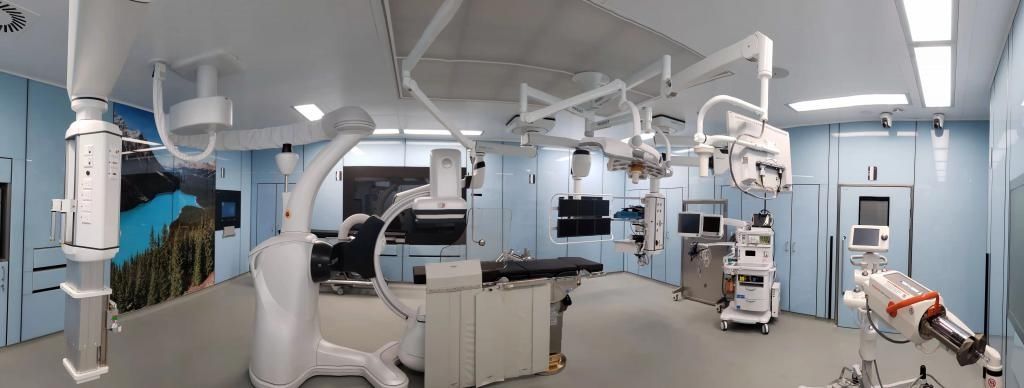
▲Hybrid operating room
“escort in the hybrid operating room and DISCIVERY IGS7 OR system” “Under the guidance of Ms. Wang’s operation, Qiao Kun’s team first performed ablation of the right middle lung and right lower lung nodules under the guidance of CT, and then changed the position, and only completely removed the upper right lung through an incision of about 3 cm. For large pulmonary nodules, the intraoperative blood loss was only 5 ml. Postoperative pathological results showed that Ms. Wang’s nodule was an early-stage adenocarcinoma.
After several days of treatment and observation, Ms. Wang recovered and was discharged from the hospital.
Qiao Kun said that in recent years, the thoracic surgery team of Shenzhen Third Hospital has been committed to customizing individualized strategies for patients with multiple pulmonary nodules, through minimally invasive thoracoscopic surgery and intraoperative CT-guided microwave ablation. Method is one of the best combinations. ” Peripheral high-risk pulmonary nodules can undergo more precise wedge resection with the help of intraoperative CT localization to avoid postoperative recurrence. For deep nodules, the ablation method can avoid unnecessary pulmonary segment or even lobectomy, and maximize the Preserve lung function.” Qiao Kun said.
Shenzhen Evening News reporter Wang Yu