In the opinion of many small partners, exercise seems to be remembered only when gaining muscle and reducing fat. In fact, the benefits of exercise are not limited to the external body. For example, to prevent the spread of the virus, it is very important to improve one’s own immunity, and reasonable and moderate exercise has played an important role in the process of improving immunity and resisting diseases. In the past few days, I have heard that some small partners have started assault training in order to improve their own immunity and even experienced excessive exercise and overtraining. This approach is not only undesirable, but also the effect will be contrary. Everything is too late, and mastering the “degree” can achieve the desired effect. Today we will talk about some of the relationship between exercise and immunity, and how to properly improve our own immunity.

Click to load the picture
After reading this article, you will gain the following four aspects
The relationship between exercise and immunity
Why excessive exercise will weaken immunity
What is the concept of moderate exercise
Other factors that affect immunity
Relationship between exercise and immunity
Exercise is a good way to improve immunity, but everything is logical, and it also pays attention to a degree , There are rules and regulations to follow, and you can’t mess around. There are many widely supported theories of the relationship between exercise and the immune system.
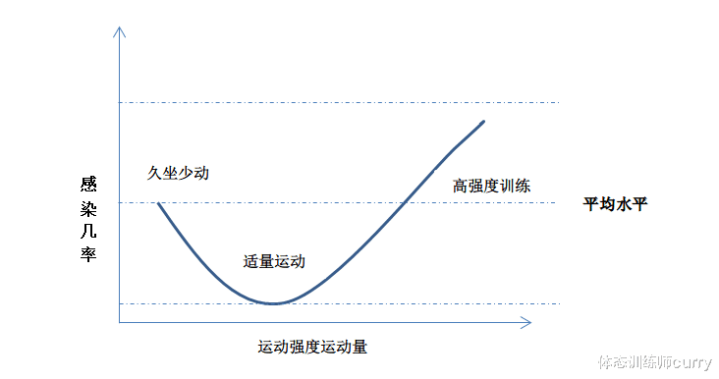
J Theory
Click to load image
< p> In 1994, Nieman et al. studied the J-shaped curve of exercise volume and upper respiratory tract infection, which well described the relationship between infection risk and exercise intensity. This study was based on sedentary people, regular exercise people and marathon people. A study of upper respiratory tract infection by the exercise intensity of athletes and other personnel [1]. Studies have shown that an individual’s exercise intensity and level will directly affect the risk of upper respiratory tract infections, such as colds and respiratory diseases, thereby increasing the probability of illness in the human body. Moderate exercise appears to reduce the risk of disease compared with a sedentary lifestyle, but high-intensity or prolonged exercise increases the risk of infection.
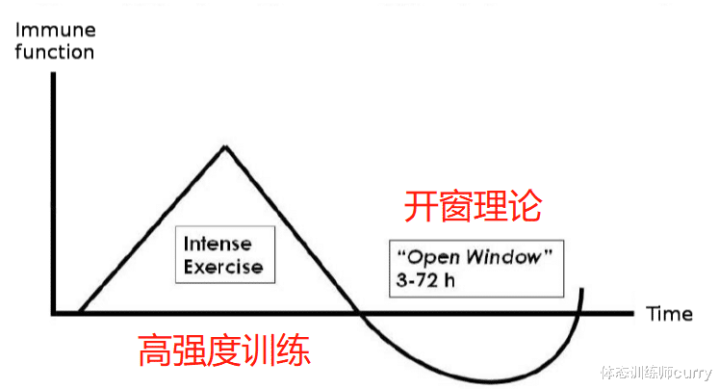
Windowing Theory
Click to load image
Although J theory shows the relationship between physical activity and upper respiratory tract infection, it does not explain why there is such a relationship from immunology. So in 2000, Nieman explained how exercise affects the human immune system through the windowing theory in a follow-up paper [2]. The windowing theory explains that within 3 to 24 hours after high-intensity training (and it may last up to 72 hours), the immune system will fail to varying degrees, allowing bacteria and viruses to take advantage of it. At this time, we call this phenomenon the fenestration theory. Although the same as the nutritional window, it occurs after training, but the window theory is more of some negative factors.

Click to load the picture
The above theories all show a truth, moderate exercise It can improve one’s physical fitness and is conducive to the improvement of the immune system, while prolonged or high-intensity exercise will make our immune system function decline, increasing the risk of the body being attacked by bacteria or viruses.
Why Excessive Exercise Can Reduce Immunity

Click to load picture
To be sure, moderate exercise stimulates the immune system and strengthens the body’s defenses. When we exercise, no matter the intensity of the exercise, the body releases cortisol, a stress hormone. In the short term, cortisol can help regenerate muscles, maintain blood sugar levels, and boost the immune system’s defenses, when matched to moderate exercise intensity. But when overtrained, cortisol is secreted in large quantities, suppressing the levels of white blood cells and other cells in the immune system, allowing the amount and function of antibodies and pro- and anti-inflammatory biochemicals such as cytokines changes, thereby interfering with the body’s ability to respond and respond to foreign bacterial and viral invasion.

Click to load the picture
At the same time, 3~24 hours after overtraining At this time, the body is in a state of fatigue. If there is no good nutritional supplementation and rest, the ability of the immune system to play its role will decline, and the human body will be more easily invaded by harmful substances such as bacteria and viruses, resulting in illness. Cortisol produced by constant stress affects the body’s digestive system, reproductive system, and even natural growth processes in addition to affecting the immune system. This is one of the reasons why many high-level athletes are more prone to colds than the average person. Therefore, for our non-professionalFor the mobilized public, moderate exercise is critical.
What is the concept of moderate exercise
WHO recommendations

Click to load image
The World Health Organization recommends that people aged 18-64 should improve cardiorespiratory, muscular and skeletal health, reduce chronic non-communicable diseases and depression , the recommendations are as follows:
Adults aged 18-64 should complete at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic physical activity per week, or accumulate at least 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic physical activity per week , or an equivalent combination of moderate and vigorous intensity activities.
Aerobic activity should last at least 10 minutes at a time.
For additional health benefits, adults should increase their aerobic activity to 300 minutes per week of moderate-intensity or 150 minutes of vigorous-intensity per week, or moderate and vigorous intensity An equivalent combination of the two activities.
At least 2 days per week should be performed with large muscle groups involved in strengthening the muscles.
The above suggestions are only suggestions for a normal exercise after having exercise habits, and are not suitable for people who have been sedentary for a long time or have many years of training experience.
Exercise recommendations for sedentary people

Click to load image
For people who are sedentary and less active without a foundation of exercise, the so-called moderate exercise is initially recommended to be measured by slightly sweating or a state of normal conversation but a little breathing during exercise. This may be a better advanced state for people who are sedentary and less active, and avoid sudden exercise or physical discomfort caused by sudden high-intensity exercise. For people who are sedentary and less active, the early stage of exercise is more about the establishment of exercise adaptability. The goal is to develop the habit of exercise and let the body gradually enter the state, and improve their immune system step by step. This kind of relaxed and stress-free exercise state is recommended for about 30 minutes at the beginning, and then it is excessive and improved to the WHO standard.
Exercise recommendations for long-term training populations

Click to load the picture
People who have been training for many years have developed the habit of exercise and adapted to a certain intensity of exercise. If you want to stay in shape, you just need to maintain a certain amount of exercise. But most people who train for a long time are people with certain target needs, or sports performance, or athletic or physical needs, or goal-oriented. In short, I still want to constantly break through my upper limit to work hard to get faster and better results. At this time, the phenomenon of window opening after exercise may occur, and the defense ability of the immune system will also decline, increasing the probability of illness.

Click to load the picture
This kind of people should pay more attention after training It is about nutritional supplements before and after training, the design of a reasonable exercise plan, adequate rest, and physical warmth after training. At any time of the day, you can perceive whether you have been in a state of overtraining. If after rest, the training intensity is still not as good as before, the overall body is fatigued, the quality of sleep is poor, emotional anxiety, and even no interest in training , may be a sign of overtraining. At this time, it is necessary to focus on adjustment and rest, and avoid forced training.
Other Factors Affecting Immunity
Exercise should be promoted, but overtraining is not advisable, especially for people whose goal is to get healthy, blind training should be avoided. In order to continuously improve and maintain the immune system. But exercise is only a part of the factors that affect the human immune system, and more factors that affect the immune system also need attention.
Stress Relief

Click to load image
< p>The level of human stress directly affects the body’s immune system. What we usually call stress is chronic stress, and this chronic stress is more likely to lead to excessive secretion of the stress hormone cortisol. The mental state is not good, the stress is high, and the endocrine disorder of the human body directly affects the quality of sleep, diet and exercise. Therefore, it is necessary to learn to regulate stress, properly relax and soothe your emotions.

Click to load image
Walk or jog outdoors with less air circulation and listen at home Music, practicing yoga, taking a hot bath or soaking your feet before going to bed, and meditating for a few minutes a day will all play a positive role in relieving your stress. Especially enough high-quality sleep is the most efficient way for the human body to relieve fatigue, and it is also the most direct way to restore cortisol to the normal range. All of the above measures canIt is very effective to improve and enhance the body’s immunity.
Balanced meal

Click to load image
< p>Although a variety of ingredients are now abundant, many people are not ideally balanced in their diet. A high-fat, high-sugar, and high-salt diet almost fills the dining table of modern people. The impact of such a dietary structure on the body is an increase in the level of chronic inflammation, which is not conducive to the improvement of the immune system. The requirement of a balanced diet is that various nutrients are ingested in a balanced and reasonable proportion. The daily caloric intake ratio of carbohydrates, protein and fat is adjusted to 5:3:2, and fresh fruits and vegetables are supplemented. Not only will the three major nutrients be fully ingested, but other vitamins and minerals will also maintain a certain intake level, which is a good support for the body’s immune system. In particular, vitamin C, vitamin D and the trace element zinc are very important for the body’s resistance. Usually, we should focus on supplementing some ingredients containing the above vitamins and minerals, such as fruits, calcium-containing products and oysters.
Other Factors

Click to load image
< p>In addition to maintaining a good mood, relieving external pressure, eating a balanced diet, exercising moderately, and getting enough sleep, you should also try your best to take protective measures when you go out, and avoid going out during flu season and other special circumstances In places with large traffic, wearing masks when going out, washing hands frequently when returning indoors, maintaining hygiene and regular disinfection in the residence environment and workplace, etc., can effectively reduce the spread and infection of bacteria and viruses, thereby improving the defense ability of the immune system in disguise. At the same time, in some special periods, it is also necessary to try to avoid long-term (more than 1 hour) aerobic exercise, heavy load resistance training and other exercise methods that cause excessive stress to the body, which will affect the normal functioning of the immune system. effect.
Conclusion

Click to load the picture
Everything has two sides, movement It is no exception. It can both promote and negatively affect our immune system. Therefore, we need to correctly understand the “scientific movement” and practice it effectively. But at the same time, exercise is only a part of the immune system. Only by implementing a balanced diet, moderate exercise, adequate sleep and maintaining a good mood will our immune system work more efficiently. , will have a good body. Do not exercise blindly, the more scientific the more efficient. Come on, everyone.