Patients with meningiomas not only experience symptoms such as headaches and vision loss, but also sometimes seizures, smell and hearing disturbances.
Sequelae after meningioma surgery
The main treatment for meningioma is surgical resection. The treatment can achieve better therapeutic effect and be cured.
Benign meningiomas have an excellent effect of total resection, but due to the location of their growth, about 17% to 50% of meningiomas cannot be fully resectioned. a cause of postoperative sequelae. There are also a few malignant meningiomas that cannot be completely resected. In both cases, radiation therapy is required after surgical resection.
Like any tumor, meningioma surgery, if some tumor remains in the primary site, may cause tumor recurrence or cause postoperative sequelae, such as disturbance of consciousness, even respiratory arrest, blood pressure drop, etc. , can also cause sustained increase in intracranial pressure. There are also new obstructive lesions such as brain tissue edema and hematoma.
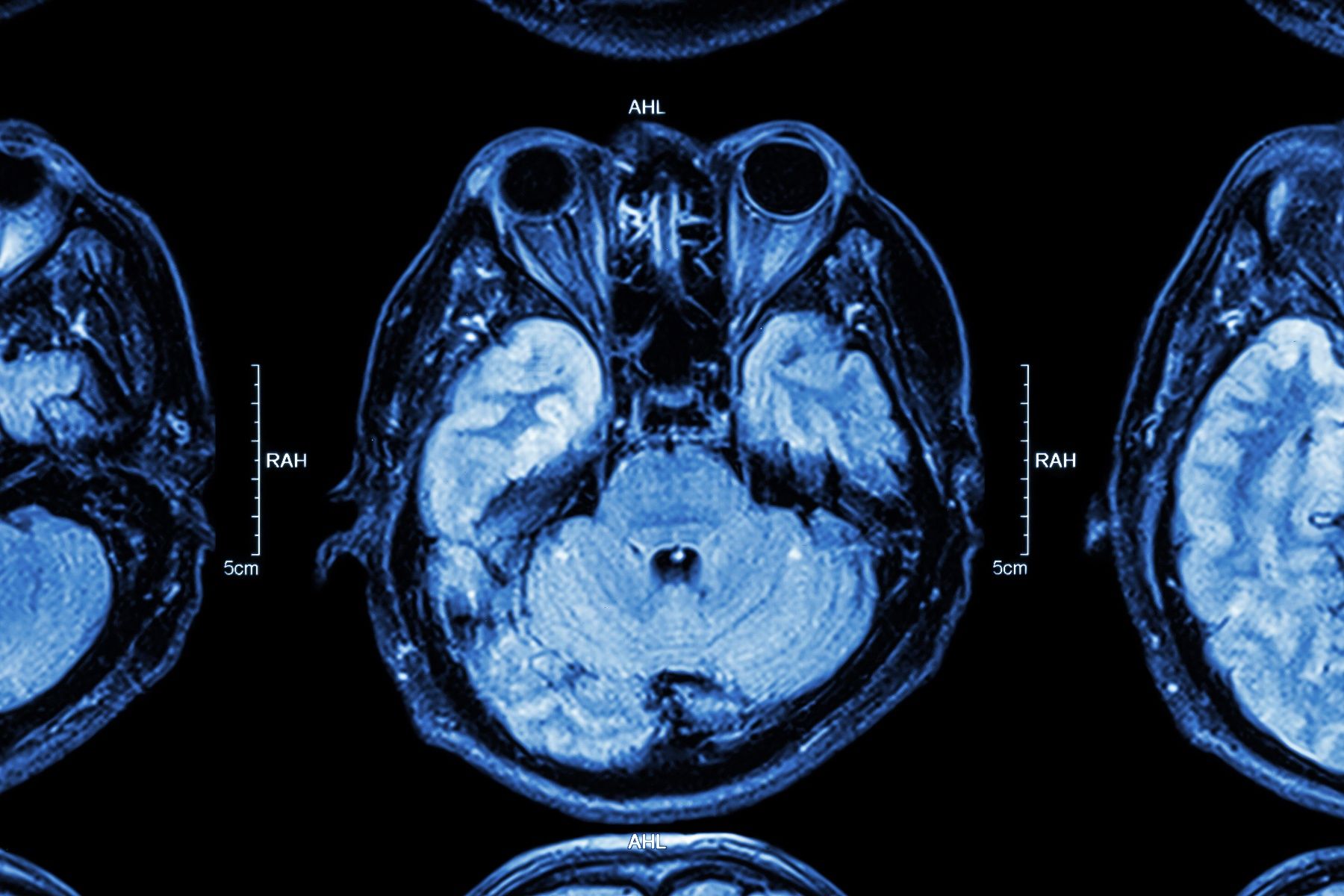
Sequelae of meningioma surgery
The surgical site of meningioma is in the brain, which controls Due to the normal functioning of the body’s organs, the risk of surgery in this area is much higher than that in other locations, and the postoperative sequelae are more unpredictable. A doctor is required to remove the brain tumor without damaging the surrounding normal tissue.
In some cases, the sequelae of brain tumor surgery are unavoidable. In the process of surgical tumor resection, due to the adhesion of tumor tissue and brain tissue or the need for surgical resection, some cranial nerve tissue is often damaged, resulting in some corresponding clinical symptoms, such as limb numbness, pain, inability to move, Symptoms such as language difficulties. However, the location of the lesion must be removed, or the brain tumor will soon recur.
In addition, during meningioma surgery, there are often unresectable residual tumors that continue to grow in the patient’s brain. Sometimes these residual tumors will continue to compress local brain tissue, causing the patient to have headaches and dizziness. and other symptoms. Surgical resection is still the best way to manage recurrent meningioma, and postoperative adjuvant chemoradiotherapy is more effective in the treatment of meningioma.

How to avoid post-meningioma sequelae
Diagnose in an experienced neurosurgery and take appropriate action treatment is particularly critical. The main treatment for meningiomas is surgical resection, which includes skull base surgery, minimally invasive craniotomy, and neuroendoscopic surgery.
The most reliable prognostic factors for meningiomas are WHO grade and degree of resection (Simpson grade). If meningiomas can be cured, the prognosis is good, and most patients have good quality of life after surgery. Surgical outcomes vary depending on the location and treatment of the meningioma. Those located in the medial sphenoid ridge, cavernous sinus, clivus and other difficult surgical sites have poor prognosis and high operative mortality. The recurrence rate of meningioma after surgery is usually between 13% and 40%, and the recurrence rate of meningioma has a great correlation with the degree of Simpson grade of resection. The recurrence rate of patients with Simpson grade I surgery was 9%, grade II was 19%, and grade III was 29%, and the recurrence rate of meningiomas also increased with the extension of follow-up time.
(The above pictures have been authorized by Baotu.com)