On February 27, 2022, the National Cancer Center released the latest cancer report in China – “2016 Cancer Incidence and Mortality in China”. Many careful friends may want to ask: how does the latest report use the data of 2016?
This is because the collection, collation and verification of national data takes a lot of time, so cancer reporting is usually delayed by 2-5 years. It can be said that this is one of the latest and most representative reports on cancer incidence and death data in China in 2016, covering about 380 million people, accounting for 27.6% of China’s total population.

So compared to previous data, what information is in the latest cancer report worth paying attention to? Follow Coco to learn about it~
1. Lung cancer is still the number one “killer”
According to the report, there were about 4.064 million new cases of malignant tumors in my country in 2016, which is equivalent to an average of more than 11,100 new cancers diagnosed every day, and an average of 7 people diagnosed every minute.
Among them, the most common cancer is still lung cancer – in 2016 alone, 828,000 people were diagnosed with lung cancer, and nearly 660,000 patients died, accounting for more than 20% and 27% of all cancers, respectively! If you want to avoid the occurrence of lung cancer, you must do a good job of prevention, especially to avoid the two major “lung-injuring factors” in life as much as possible:
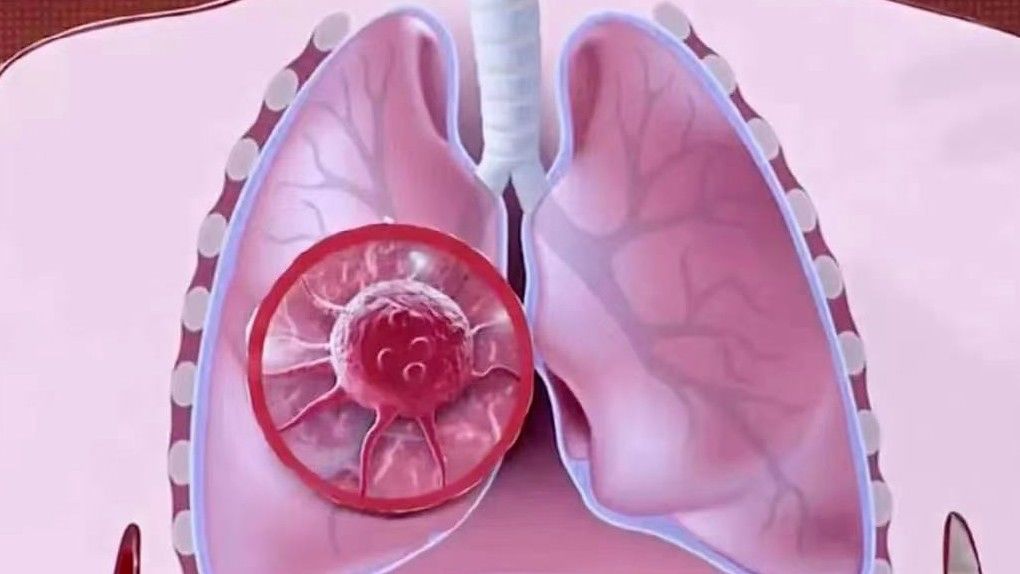
1.Tobacco gas
Smoking is one of the most important causes of lung cancer, with 87% of lung cancer deaths due to smoking. Smoking can produce more than 40 carcinogens, such as nicotine, carbon monoxide, cigarette tar and other carcinogens, which can cause DNA damage in bronchial epithelial cells through different mechanisms, activate certain oncogenes, and increase the risk of lung cancer.
What’s more important is that secondhand smoke can be even more harmful than smoking – it produces more carcinogens and the harm lasts longer. So, whether it’s for yourself or your family, stop smoking!

2.Fume
The cooking fumes can also contain a lot of harmful substances, especially when stir-frying, frying, and grilling food at high temperature, a large amount of carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, ammonia oxide and the first-class carcinogen benzopyrene may be Are released, these substances are inhaled into the lungs for a long time and can also cause cumulative damage to the lungs.
Data show that people who have been exposed to oil fumes for a long time are 2-3 times more likely to develop lung cancer than normal people! This is also an important reason for the high incidence of lung cancer in women. Therefore, everyone must remember to turn on the range hood when cooking, and also open the windows for ventilation to reduce the damage to the lungs by the fumes.

2. The previously high incidence of cancer is declining
But these bad eating habits still need to be vigilant
The latest cancer report also announced good news: from the perspective of individual cancer trends, esophagus cancer, stomach cancer and liver cancer, three of the gastrointestinal cancers with high incidence in the past, have shown a downward trend in incidence and mortality.
◎The incidence of liver cancer is decreasing: it may be due to decreased intake of aflatoxin-contaminated food, improved water quality, and hepatitis B vaccination.
◎The mortality rate of esophageal cancer and gastric cancer decreased: it may be the result that endoscopic screening is more conducive to early diagnosis.
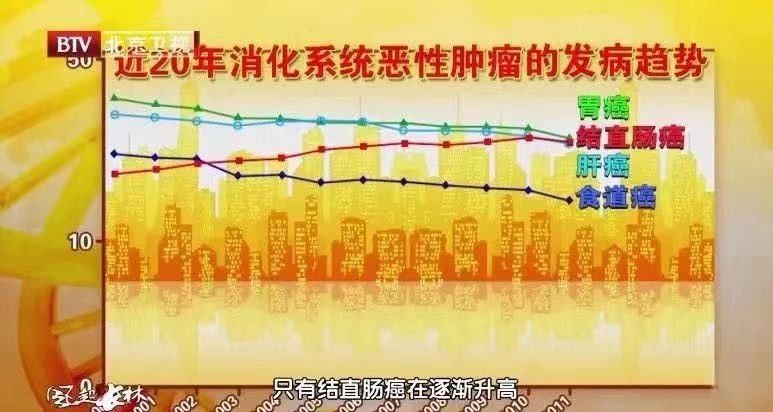
It is not difficult to find that with the development of China’s economy, people’s living standards have improved, and medical and health conditions have improved, which have reduced the incidence and mortality of cancer to a certain extent. But as a “country on the tip of the tongue”, we still have to be alert to some bad eating habits, so as not to “eat” gastrointestinal tumors, such as:
1. Eating too hot: increased risk of esophageal cancer
Chinese people pay attention to “eat while it’s hot and drink it while it’s hot”, but be careful, when the temperature of the food is too high, it can burn the esophageal mucosa and cause inflammation. In the long-term, the esophagus is in the process of continuous repair and damage, and gene mutations may occur, which may induce esophageal cancer.
Actually, the World Health Organization has already listed food above 65°C (it will feel a little hot in the mouth) as a Category 2A carcinogen. Therefore, it is best to leave the food just out of the pot for a period of time, and eat it when it does not feel hot to the mouth.

2. Love to eat pickled food: increase the risk of stomach cancer
Preserved foods such as salted meat and salted fish are easy to cook and easy to eat, so they are loved by many people. However, it should be noted that there are often a large amount of nitrite in preserved foods, especially in preserved meat products, which may directly produce nitrosamines, which will increase the risk of cancer if eaten for a long time.
As early as 2017, the International Center for Research on Cancer listed Chinese-style salted fish as a first-class carcinogen. Therefore, in daily life, we should eat less pickled food and more fresh food; in addition, long-standing green leafy vegetables, long-cooked hot pot soup, and freshly cooked pickled vegetables are all “gathering places” for nitrite. Be careful too.

3. Love drinking: increase the risk of liver cancer
The main component of alcohol is ethanol. During the metabolism of ethanol and its derivatives, a large number of inflammatory substances and oxides will be produced, which can cause irreversible damage to the liver.
Long-term drinking or heavy drinking in a short period of time can cause alcoholic hepatitis, causing repeated fatty degeneration, necrosis and regeneration of liver cells, which may eventually lead to liver cirrhosis and even liver cancer. Therefore, if we can not drink, we must not drink.

3. Cancer caused by bad habits is increasing
Let’s see if you got hit?
The bad news to watch out for is that the incidence and death rates of colorectal cancer, prostate cancer, breast cancer and other cancers are on the rise, and this may be related to the bad habits of lack of exercise in life!
People who lack exercise have a slower metabolism, and some waste substances are easy to accumulate in the body, causing inflammation. Repeated inflammation can cause a large number of cell damage, and cells may undergo gene mutation and cause cancer in the process of “injury-repair”.
In addition, long-term lack of exercise is more likely to lead to obesity. Obesity itself is a chronic inflammatory state of the body, which easily induces the growth of cancer cells; and obesity may also lead to metabolic disorders and hormone imbalances in the body, increasing the risk of breast cancer, prostate cancer and other cancers.

The National Cancer Institute found that adults who exercised the most had an average 7% lower chance of developing cancer compared with adults who exercised the least. The WHO’s global guidelines on physical activity and resting behaviour also state that around 5 hours of physical activity per week could help prevent 5 million deaths globally each year.
【Suggestion】
◎Adults: At least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise (such as brisk walking, dancing, etc.), or 75 minutes of high-intensity exercise (biking, jogging, tennis, etc.) per week;
◎Seniors over 65 years old: moderate or higher-intensity physical activity is recommended at least 3 days a week to enhance balance, coordination and muscle strength.

4. Stay away from cancer
Don’t ignore these 8 screenings!
In general, the overall number of new cases and deaths from malignant tumors in 2016 was higher than in previous years. But you don’t have to panic too much. Although cancer is scary, it doesn’t happen suddenly, and it usually takes several years or even a dozen years to develop.
In this process, in addition to correcting bad living and eating habits and avoiding high-risk factors of cancer, we can also achieve early detection and early treatment through physical examination, and timely nip cancer in the bud! The following Cocoa introduces the “gold standard” of screening for 8 types of high-risk cancers:

◎Lung cancer screening: People over 50 years old should do low-dose spiral CT once a year, which is helpful for early detection of lung cancer; people with a family history of lung cancer and long-term smokers are high-risk groups of lung cancer, and it is recommended to start early Inspection of.
◎Colorectal cancer screening: It is recommended for the general population to have an anorectal examination every year after the age of 50; while people with familial polyposis, people with inflammatory bowel disease, and people with poor diet are all high-risk groups. It is recommended to advance to the age of 30 and have a colonoscopy every year.
◎Gastric cancer screening: It is recommended that ordinary people have their first gastroscopy at the age of 40, and once every two years after everything is normal; people with underlying diseases or high-risk groups such as family history should undergo gastroscopy once a year.
◎Liver cancer screening: People with a history of chronic hepatitis and family history, as well as people with diabetes, obesity, and alcoholism are at high risk of liver cancer. It is recommended to have a color Doppler ultrasound every six months, and blood tests for alpha-fetoprotein and liver function to evaluate liver status.
◎Esophageal cancer screening: Esophageal cancer is easy to target people who are over 40 years old, have a family history of gastrointestinal cancer, and have a history or symptoms of upper gastrointestinal disease. Esophageal endoscopy every 1 to 2 years is recommended for these populations.
◎ Breast cancer screening: Under normal circumstances, young women can do breast B-ultrasound examination; after the age of 40, it is best to have a mammography examination every 1-2 years.

◎Cervical cancer screening: The real effective screening for cervical cancer is TCT, that is, liquid-based thin-layer cell detection. The detection rate of cervical cancer cells can reach more than 90%. It is recommended that women aged 25 to 29 have a TCT examination every year; women aged 30 to 65 need to do TCT combined with HPV testing.
◎Prostate cancer screening: The incidence of prostate cancer tends to increase gradually after the age of 55, and screening every two years is recommended. An effective method for screening prostate cancer is color Doppler ultrasound + prostate-specific antigen (PSA).

(I am the official WeChat account of a big doctor)