Abstract: For adults with epistaxis, only 10% of them need treatment. History of drinking, taking anticoagulants, hypertension, and allergic rhinitis are important risk factors for epistaxis.

1. Do you know what is nosebleed?

Epistaxis is one of the common clinical symptoms, which can be caused by nasal diseases, systemic diseases or caused by trauma. In adults, only 10% of patients require treatment. Studies have shown that drinking history, taking anticoagulant drugs, hypertension, and allergic rhinitis are important risk factors for epistaxis. Early intervention is of great significance to prevent and reduce the incidence of epistaxis.
2. Correctly handle epistaxis
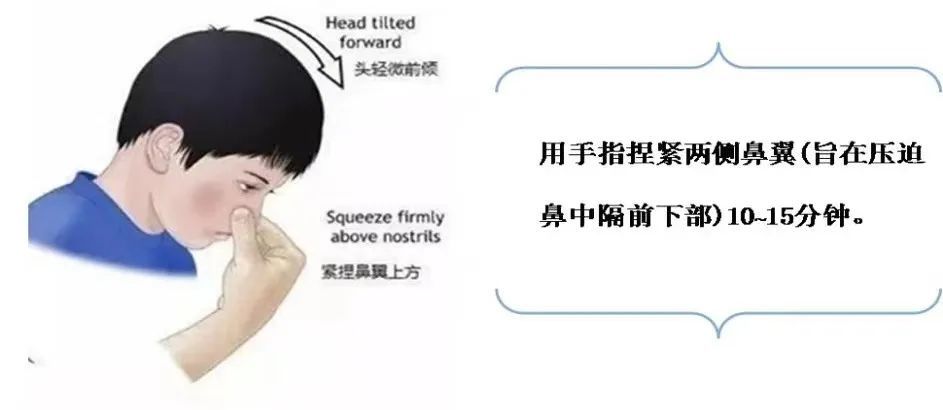
1. Compression to stop bleeding: You can press your fingers to stop bleeding On the side of the nose, open your mouth to breathe, and put an ice pack or cold towel on the nose to constrict blood vessels and reduce bleeding.
2. The body leans forward slightly, the blood flowing out will accumulate and coagulate, which is beneficial to local hemostasis.
3. If the bleeding is repeated or cannot stop, you should seek medical attention immediately! ! !
3. Common hemostasis mistakes

Habitual head up: once the blood flows back, swallow In the stomach, it will irritate the gastric mucosa, cause stomach discomfort, nausea and vomiting, and aggravate bleeding.
Blind stuffing: Usually people use a tissue to plug the nostrils, thinking that this will stop the bleeding. Instead, this practice can damage the nasal mucosa and worsen nosebleeds.
IV. Prevention of epistaxis
1. Open windows for ventilation, maintain indoor temperature at 18~20℃, and air humidity should be ≥60%.
2. Pay attention to nasal hygiene, correct bad habits such as picking your nose, rubbing your nose, and blowing your nose hard.
3. If there are nasal diseases such as sinusitis, rhinitis, nasal polyps, etc., the primary disease should be actively treated.
4. Use medicines as prescribed by a doctor, and do not use blood-activating medicines without permission or adjust the dosage of medicines at will, such as aspirin, salvia, ginseng, Panax notoginseng, etc.
5. Elderly patients with epistaxis must be treated with high blood pressure, coronary heart disease, bronchitis, etc. Hypertensive patients should control their blood pressure as soon as possible, observe the changes in their condition, and seek medical attention in time
6. During the period of epistaxis, do not eat or drink too much, and do not wash your hair, take a bath or use a sauna with too much hot water.