
With the increase of precipitation in Zhangzhou
Wild mushrooms enter the peak growth season
Recently, there have been many occurrences in our province
Poisoning incidents caused by eating wild mushrooms
On the 22nd, Zhangzhou CDC urgently reminded:
There are many kinds of wild mushrooms, and it is difficult for ordinary people to distinguish them
Among them, the number one poison king “white poisonous umbrella”
is distributed in many places in Zhangzhou

Please don’t pick, buy, sell or eat by yourself!
Zhangzhou Center for Disease Control and Prevention reminds the general public: There are many kinds of wild mushrooms, and it is difficult for ordinary people to distinguish whether they are poisonous or not. Once poisoned, the mortality rate is very high. Inadvertently endangering life and health, in the face of these wild “deliciousness”, we must resolutely do not pick, sell, or eat.
Accidental ingestion of poisonous mushrooms can lead to vomiting, diarrhea, or death.
There are more than 100 kinds of poisonous mushrooms in my country, and there are at least 10 common ones that can cause death, such as Umbrella with brown scales, white poisonous umbrella, brown-handled white poisonous umbrella, poisonous umbrella, remnant spotted poisonous umbrella, poisonous powder folded mushroom, autumn-born helmet spore umbrella, black folded umbrella with covered feet, deer flower mushroom, etc.
The toxins contained in poisonous mushrooms are mushroom toxins. The symptoms of poisoning can be divided into 5 types: gastrointestinal type, neuropsychiatric type, hemolytic type, organ damage type, and photoallergic dermatitis type. The incubation period of poisonous mushroom poisoning varies from 10 minutes to 30 hours. The clinical manifestations of poisoning are complex and diverse. Generally, the early symptoms of poisoning are nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, diarrhea and other symptoms. In severe cases, it can lead to convulsions, convulsions, hallucinations, and even death from respiratory failure and heart failure. There is no effective treatment for poisonous mushroom poisoning, and the fatality rate is extremely high.
Inedible wild mushrooms
How to save yourself in case of accidental mushroom poisoning?
In case of mushroom poisoning, drink a lot of warm water or dilute salt water immediately, put your finger or toothbrush handle into the throat to induce vomiting, and send it to the nearest medical unit as soon as possible for vomiting, gastric lavage, and catharsis. to expel toxins as quickly as possible. It is best to bring the remaining mushroom samples with you when you go to the doctor for further diagnosis.
Some of the poisoned patients relieved their symptoms after conventional treatment and seemed to have recovered. In fact, they entered the “false recovery period”. After about 1-2 days, the condition suddenly deteriorated and was life-threatening. Therefore, patients with mushroom poisoning should be observed for 1-2 days after the symptoms disappear. If there are symptoms of discomfort, they should seek medical attention immediately to prevent delayed treatment due to false recovery.
In order to avoid poisonous mushroom poisoning, we advocate: do not pick, do not buy, do not eat wild mushrooms.
Don’t pick it
There is no simple and easy identification method to identify whether wild poisonous mushrooms are poisonous or not. The fundamental way to prevent poisonous mushroom poisoning is not to eat wild mushrooms to avoid accidents. endanger health or even life safety.
Don’t buy
Be careful not to buy mushrooms from roadside vendors, even in regular markets, don’t let your guard down and try not to buy wild mushrooms.
Do not eat
In order to avoid the occurrence of poisonous mushroom poisoning, families should eat wild mushrooms with caution. Do not process and eat wild mushrooms for group dinners, catering services, and folk tourism.
Deadly Amanita (Amanita exitialis ZhuL.Yang & THLi), commonly known as “white poisonous umbrella”, this species was first recognized by the scientific community in Guangzhou in March 2000 because of this “highly poisonous killer”, which caused All 9 migrant workers died of poisoning. In order to warn future generations, Professor Yang Zhuliang of Kunming Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences, and Professor Li Taihui of Guangdong Institute of Microbiology jointly named the species “Deadly Amanita”. Since this species can cause acute liver damage, it has been found to have caused at least 30 tragedies in my country, resulting in the poisoning of more than 100 people, of which more than 60 people died. p>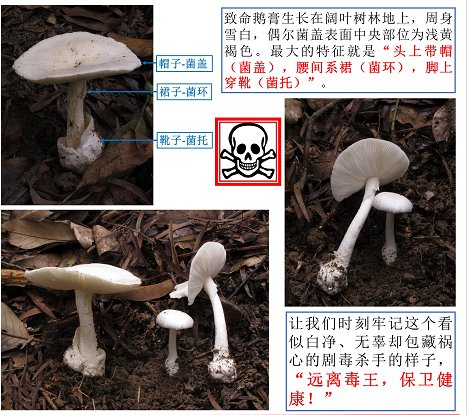
Source: Zhangzhou CDC
Editor of this issue: Cai Nannan and Zheng Sinan
Director on duty: Lin Kun