[Source: Huaihua News Network]
With the popularization of physical examinations, more and more people, especially female friends, find thyroid nodules during neck B overtime Very nervous and overwhelmed. Do you really know about thyroid nodules? Next, Dr. Tang Hongming, director of general surgery in Jingzhou branch of Huaihua Second People’s Hospital, will unveil the mystery of thyroid nodules for everyone.
I. What is a thyroid nodule?
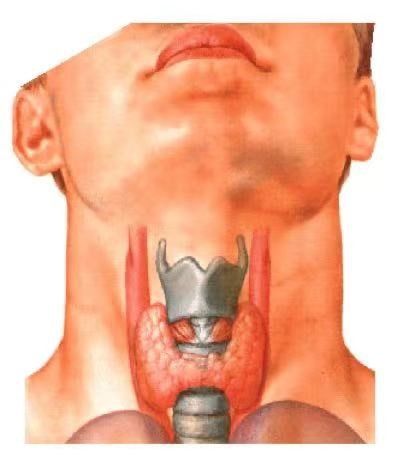
A thyroid nodule is a lump in the thyroid gland, ranging in size from as small as 1mm to large to several centimeters. Large nodules move up and down with the thyroid gland when swallowing, which is a common and frequent clinical disease. There are a variety of thyroid diseases clinically, such as thyroid degeneration, inflammation, autoimmunity, and neoplasms, which can all present as nodules. Thyroid nodules can be single or multiple, and the incidence of multiple nodules is higher than that of single nodules, and women are higher than men.
Second, why do I get thyroid nodules?
1. It is related to the excessive pressure of work, study and life, long-term anger, anxiety or anxiety, and physical factors such as women’s physiological characteristics such as menstruation, pregnancy, childbirth, breastfeeding, etc. .
2. Iodine deficiency: The intake of iodine is too low or the absorption is not good, which affects the synthesis and secretion of thyroid hormones, resulting in abnormal levels of thyroid hormones in the body, resulting in hyperplastic nodular goiter.
3. Genetic factors: According to research, genetic factors are one of the important reasons. The patient’s hereditary enzyme deficiency, hormone synthesis disorder, thyroid hormones in thyroglobulin cannot be separated, and blood thyroid hormones are lacking, resulting in Thyroid enlargement.
4. Radiation factor: Radiation can cause abnormal division of thyroid cells, cell proliferation, and at the same time, the secretion function of the thyroid gland is reduced, resulting in a large amount of thyrotropin secretion, causing the thyroid gland to enlarge and even become cancerous.
5. Inflammation: Due to the inflammation of the thyroid itself, the density of the thyroid increases, resulting in the formation of inflammatory thyroid nodules, the most common such as subacute thyroiditis and Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
3. What are the manifestations of thyroid nodules?
Most patients with thyroid nodules are asymptomatic. When combined with abnormal thyroid function, corresponding symptoms may appear. If the thyroid nodule compresses surrounding tissue, it can present with hoarseness, a feeling of air pressure, and difficulty breathing and swallowing. (Most patients with thyroid nodules are found only through thyroid B-ultrasound during physical examination)
4. What to do with thyroid nodules
< img class="content_title" height="300" layout="responsive" sizes="(min-width: 320px) 320px, 100vw" src="https://p0.ssl.img.360kuai.com/t015b0a5017c2ec2328.jpg" width="600">
V. Treatment of benign thyroid nodules
Most benign thyroid nodules only require regular follow-up , no special treatment is required. In rare cases, surgery, radioactive iodine therapy, or other treatments are options. Traditional Chinese medicine can effectively inhibit the further enlargement or reduction of nodules through the treatment of soothing the liver and regulating qi, resolving phlegm and removing blood stasis, and achieving good curative effect. Benign thyroid nodules that meet surgical indications can be treated with traditional thyroid (lobe) resection, endoscopic-assisted small incision thyroidectomy, endoscopic thyroidectomy and percutaneous thermal ablation of thyroid nodules. Specific guidance from a professional physician is required.
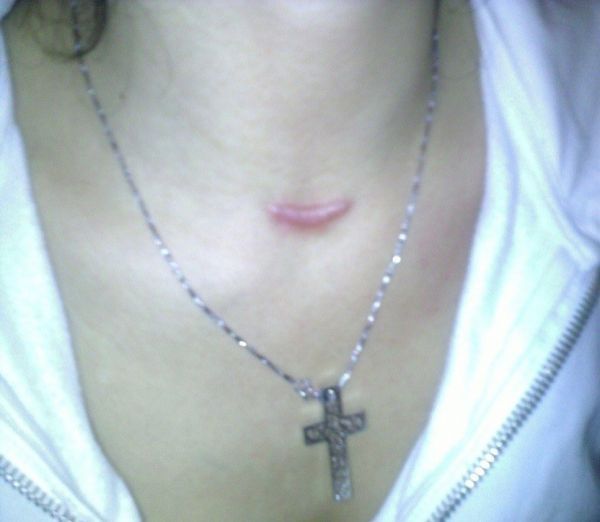
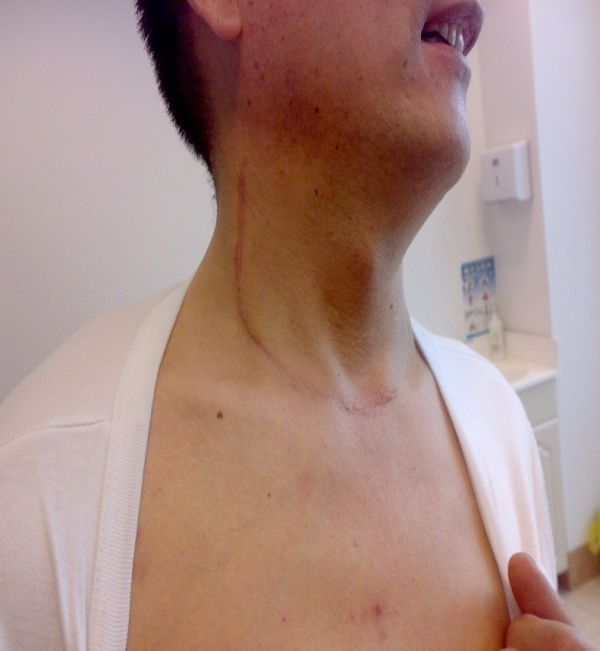
Six. What are the treatments for thyroid cancer?
The main treatments include surgery, endocrine therapy, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy. Once thyroid cancer is diagnosed, surgery is the treatment of choice. Endocrine therapy is required after surgery, that is, taking thyroid hormone for suppressive replacement therapy, and follow-up of thyroid function and thyroglobulin to prevent the recurrence of thyroid cancer. For thyroid cancer with metastases, radioactive 131-iodine ablation can be used after surgery to eliminate residual thyroid tumor cells and prevent tumor metastasis or recurrence. Medicines for the treatment of thyroid tumors in internal medicine have not yet been widely used in China.
7. Patients with thyroid nodules should be followed up regularly
Because of the uncertainty of benign and malignant thyroid nodules and their high possibility of malignant transformation, so Regular follow-up is particularly important for dynamic understanding of nodules, detection of malignant tendency, and timely intervention. For most benign thyroid nodules, follow-up can be performed every 6 to 12 months. For suspected malignant or malignant nodules that have not yet received treatment, the follow-up interval can be shortened.
VIII. What should patients with thyroid nodules pay attention to in terms of diet?
Avoid eating spicy and stimulating foods, such as ginger, chili, pepper, etc. ; Avoid or reduce the intake of fried and barbecued foods; Quit smoking and alcohol; Reduce the intake of iodine-rich seafood, such as sea cucumbers, kelp, sea shrimp, sea fish, etc., and also reduce the intake of iodine-containing salts Intake, or you can buy non-iodized salt and use iodine-containing salt alternately; eat more vitamin-rich and protein-rich foods, such as vegetables, fruits, lean meat, etc.; maintain adequate sleep and a good mood It is also very necessary.
(Correspondent: Tang Hongming)
Disclaimer: The copyright of this article belongs to the original author. If the source is wrong or your legal rights are violated, you can contact us by email Get in touch and we will deal with it in time. Email address: [email protected]