Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a chronic bronchitis and/or emphysema characterized by airflow obstruction, which can further develop into pulmonary heart disease and respiratory failure. It is a common chronic respiratory disease. Typical clinical manifestations include the following:
1. Chronic cough, which can be manifested as obvious cough during the day and coughing at night;
2. Sputum, usually white mucus, Occasionally bloodshot, more often in the morning;
3. Shortness of breath or dyspnea, which appeared early during activity, and then gradually increased;
4. Wheezing and chest tightness, acute exacerbation of the condition
5. Others such as fatigue, weight loss, etc., are complications of severe illness.
The cause of COPD
Currently the most common and most important cause is long-term smoking. In addition, long-term inhalation of occupational dust and chemical gases will also increase the risk of COPD . Genetics, age and gender, lung growth and development, socioeconomic status, asthma, chronic bronchitis, and infection are also factors that affect the onset or worsening of COPD.
Assessment of COPD
The COPD classification usually refers to the COPD pulmonary function classification, which is mainly divided into 4 grades. The percentage of predicted air volume is graded, called the percentage of predicted F1V1, which can classify patients with COPD into mild, moderate, severe, and very severe.
1. Mild: The estimated value of lung function test within 1 second is ≥80%, mainly manifested as asthma on the second floor, but usually does not seriously affect life;
2. Moderate Severity: The estimated value of lung function test within 1 second is ≥50%, while <80%, mainly manifested as asthma on the first floor, but some mild housework can be done, such as washing clothes, brushing shoes, etc.;
3. Severe: The estimated value of lung function test within 1 second is greater than or equal to 30%, and at the same time < 50%, mainly manifested as a little activity, such as walking on a flat road, going to the toilet, and wearing clothes, it will cause asthma, unable to move when it is onset, At the same time, there are certain complications;
4. Very severe: The estimated value of pulmonary function test within 1 second is <30%, or the estimated value of pulmonary function test within 1 second is <50% and accompanied by respiratory failure , mainly manifested as asthma, palpitation, inability to take care of life in a calm state, and often accompanied by some serious complications.
Respiratory rehabilitation for COPD:
1. Respiratory exercise training
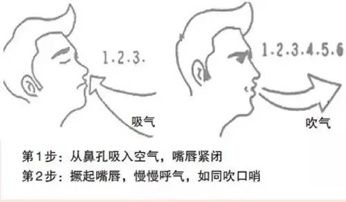
Breathing exercises include pursed lip breathing and diaphragmatic breathing. First, the pursed lip breathing exercise. Slowly inhale deeply through your nose, then pursed your lips to do a flute-style exhalation. The ratio of inhalation to exhalation time is 1:2 or 1:3, 10 minutes each time, 3 to 4 times a day. This method slows down the rate of exhalation, prevents the airway from collapsing during breathing, and helps increase ventilation. Second, the diaphragm breathing exercise. Take the supine or sitting position, relax the whole body, inhale through the nose, exhale through the mouth, put one hand on the abdomen and the other hand on the chest, try to straighten the abdomen when inhaling, or press the abdomen with hands, and when exhaling sink, try to exhale as much as possible. Generally, inhale for 2 seconds, exhale for 4~6 seconds, the ratio of inhalation to exhalation time is 1:2 or 1:3, and the breathing rate is kept at 7~8 times/min, 2~3 times a day. This method helps to strengthen the body’s diaphragmatic activity and increase lung ventilation.
2. Aerobic training
Aerobic exercise can promote the increase of patients’ cardiorespiratory endurance and improve patients’ easy asthma or breathing difficulties. Including brisk walking, jogging, swimming, cycling and other exercise methods, the training intensity should not be too large, stop when the difficulty in breathing is slightly serious, 3 to 4 times a week. Each training time should be at least 15 to 20 minutes. Using a bronchodilator spray 10 to 15 minutes before exercise can relieve exercise-induced shortness of breath and wheezing.
3. Cough and expectoration training
Effective cough and expectoration training can avoid sputum accumulation and subsequent complications. The correct way is to sit up straight as much as possible, after a deep inhalation, press the abdomen with both hands, lean forward slightly 20-45 degrees, cough continuously, contract the abdominal muscles when coughing, and forcefully expel the phlegm deep in the lungs. Cough training can be combined with postural changes, chest tapping, and aerosol inhalation for better results.
Prevention of COPD

COPD is closely related to smoking and inhalation of harmful particles Therefore, the prevention of COPD should start from the source of these harmful particles. Patients who smoke should stop smoking, and people who inhale second-hand smoke should pay attention to avoid the effects of second-hand smoke. In daily life, avoid the inhalation of harmful particulate matter. Such as cooking fumes from housewives, using biofuels, etc., patients should try their best to take protective measures, or change to some other clean fuels. Patients in the working environment of smoke inhalation should actively take protective measures and take some dust-proof measures.