Snoring is a common occurrence in people’s sleep. Many people think that snoring is the result of good sleep quality, but this is not the case. There are two types of snoring, one is benign snoring and the other is malignant snoring. Benign snoring refers to the sound of snoring that is uniform and regular, and that changes with sleeping position. Malignant snoring is not only loud, but also has apnea in the process, which is medically called obstructive sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome. This kind of snoring is very scary and has the potential to take our lives in our sleep.

What is apnea?
After a person falls asleep, the muscles of the whole body will relax, and the muscles of the head are no exception. The loose muscles and uvula press down the airway, narrowing the airway. When breathing, the airflow through the narrowed airway creates a vibrating vortex that produces a snoring sound. When the throat muscles relax enough to completely compress the airway, airflow cannot pass through, and apnea occurs.

Why is apnea fatal?
During apnea, the airway is blocked, and the patient’s blood oxygen drops significantly. Hypoxia can irritate the human body’s center, wake up the human body, and then adjust breathing. However, in particularly severe and prolonged airway obstruction, patients may not have time to adjust their breathing during sleep, resulting in sudden death.
What are the criteria for judging sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome?
The longer the breathing pause, the lower the blood oxygen saturation and the higher the risk of sudden death. Under normal circumstances, the blood oxygen saturation of the human body is not lower than 92%, and if it is continuously lower than 90%, it will cause damage to multiple organs. The more the number of apnea, the greater the harm to the human body.
Light pauses: 5 to 15 pauses per hour with a minimum oxygen saturation of 85 to 90.
Moderate pauses: 16 to 30 pauses per hour with a minimum oxygen saturation between 80 and 84.
Heavy pauses: More than 30 pauses per hour.
What are the symptoms of apnea?
There are eight major symptoms of apnea, and the most diagnostic value is daytime sleepiness. Daytime sleepiness was classified as mild, moderate, and severe. Severe drowsiness is the ability to fall asleep even when receiving continuous stimulation from the outside world, which can easily lead to vicious consequences such as traffic accidents. In addition, when no other cause can be found for symptoms such as sleeplessness, dry mouth when waking up, memory loss, high blood pressure, increased nocturia, colic, and sexual dysfunction, it may be caused by sleep apnea.
Stretching out your tongue 200 times a day will keep you away from snoring?
Sticking out your tongue 200 times a day will help you snoring, but you must not stay away from snoring. Stretching the tongue is an oropharyngeal muscle training. Studies have shown that training for more than half a year or a year can reduce the index of apnea and hypopnea to less than 50%.
Apnea enters a pathological state, and the most important treatment method is ventilator therapy. The principle of the ventilator is to generate positive pressure gas through the machine to help the patient keep the airway open.
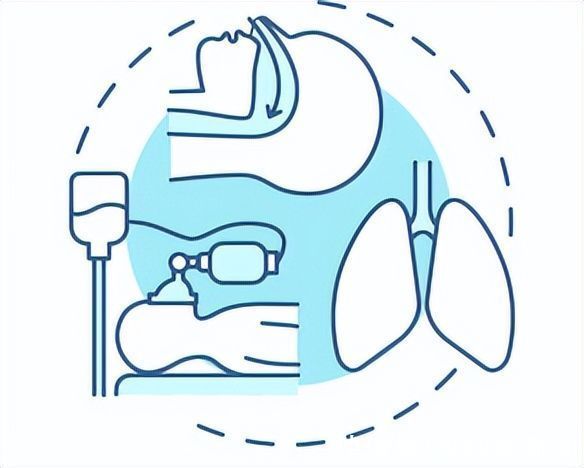
Special Note: The ventilator needs to be used under the guidance of a doctor. After the doctor adjusts to the minimum pressure that can open the airway, it is monitored in the hospital for one night, and it can be used after it is safe.
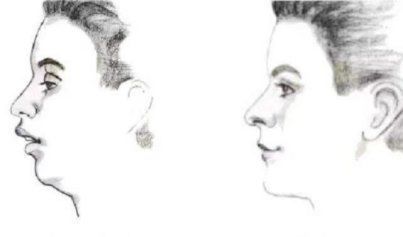
Are people with small noses, thin upper lip, and short chin at greater risk of sudden death at night?
Face shape is a very important piece of evidence for the diagnosis and screening of sleep-disordered breathing. A small nose, thin upper lip, and short chin are prone to narrow airways, which are important signs of sleep apnea.
Is drinking and snoring more deadly?
There is a strong link between drinking and snoring. When the amount of alcohol consumption is relatively large, it will affect the excitement of the central nervous system. The degree of muscle relaxation is closely related to the depth of sleep. After drinking, the patient sleeps deeply, the muscles are more relaxed, the symptoms of apnea are more serious, the central nervous system is not easy to wake up, and the risk is increased. In addition, when snoring, the chest cavity is under huge negative pressure. If you sleep immediately after being drunk, the contents of the abdomen will flow back, which may lead to aspiration pneumonia in light cases, and suffocation in heavy cases.

Special note: General anesthesia is prone to hypoxia, asphyxia, apnea and hypopnea syndrome Patients with symptoms must tell their medical history truthfully before surgery.
Are children snoring worse than adults?
This statement is correct. The incidence of snoring in children is not low, and parents must pay attention to it. The characteristics of snoring in children are not obvious, most of which are characterized by thick breathing, panting, mouth breathing, sleeping on the stomach, tossing and turning, and wetting the bed at night at the age of eight or nine.
The main cause of snoring in children is adenoid hypertrophy. Adenoids are lymphoid tissue located at the junction of the nasal and pharyngeal cavities. Adenoids begin to develop in children at the age of two or three, peak at seven or eight years old, and begin to shrink after ten years of age. Abnormal growth and hypertrophy of adenoids can cause sleep apnea.
Special reminder: Adenoid hypertrophy should seek medical treatment as soon as possible for scientific treatment.

Who are the high-risk groups for sleep apnea?
Middle-aged men, smokers, obese people, and patients with nasopharyngeal diseases are all high-risk groups for sleep apnea.