My parents taught us from childhood
eat more vitamins
To grow up healthy
Like 26 letters
Vitamins also have ABCDE and more
We all know we need to make up for it
But how to make up for it specifically
What to make up
What do they do?
Let’s talk about it today
Important to our bones and health
Vitamin D
Learn more about it
01
Vitamin D in human body weight
What role does it play?
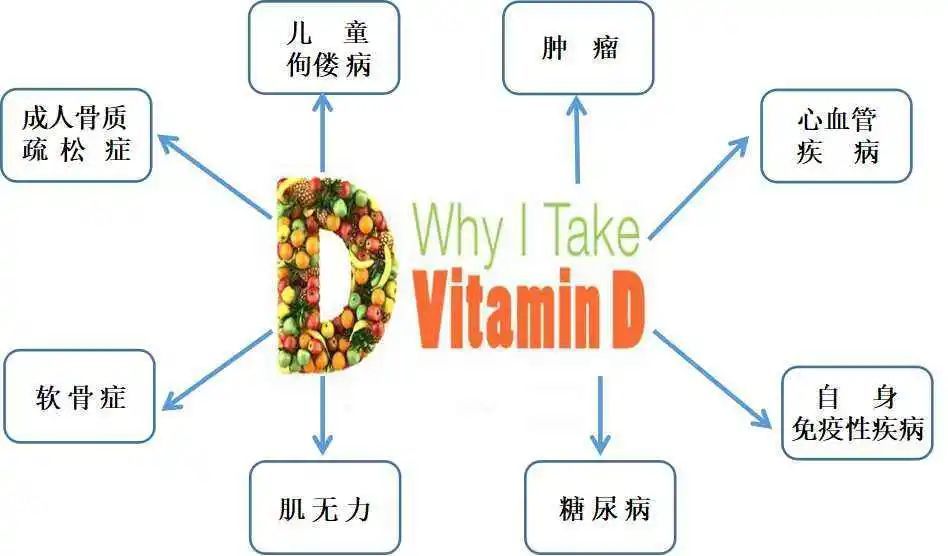
The main physiological role of vitamin D and its metabolites is to ensure bone health and normal neuromuscular function. It maintains normal blood calcium and phosphorus levels by promoting calcium and phosphorus absorption in the intestine and inhibiting parathyroid hormone release.
Severe vitamin D deficiency and metabolic abnormalities can lead to rickets/osteomalacia; vitamin D deficiency is closely related to osteoporosis and its fractures.
The elderly may have vitamin D nutritional deficiencies, reduced production and insufficient action of active vitamin D, and are prone to complications such as sarcopenia, frailty, and increased risk of falls. Vitamin D is also associated with type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and some immune and tumor diseases.
02
What are the sources of vitamin D?
Human vitamin D mainly comes from vitamin D3, which is produced by the skin after being irradiated by ultraviolet rays in the sun. Another source is food, including plant food and animal food, but there are very few types of food containing vitamin D. Foods (such as mushrooms exposed to sunlight) are rich in vitamin D2, while animal foods (such as wild fatty marine fish) are rich in vitamin D3.
Vitamin D3 produced by sun-exposed skin and vitamin D ingested from food needs to be converted into active vitamin D by the liver and kidneys in order to play its role.

03
How to Know Your Vitamin D
Is it enough?
The detection of serum 25OHD level is recognized as the most reasonable indicator to reflect vitamin D status, and it is also available in our hospital. Most international and domestic institutions and experts believe that: serum 25OHD <20ug/L (50nmol/L) is vitamin D deficiency, 20~30ug/L (50~75nmol/L) is vitamin D deficiency, >30ug/L (>75nmol/L) L) is sufficient for vitamin D, and <10ug/L (<25nmol/L) is severe deficiency.
The following people
Vitamin D levels should be monitored
Pregnant and lactating women, older adults with a history of falls and/or non-traumatic fractures, people with limited sunlight (indoor work, night work, etc.), obese children and adults (BMI ≥ 30kg/㎡ ), people undergoing bariatric surgery, and patients with bone metabolism-related diseases, liver and kidney insufficiency, gastrointestinal absorption disorders, and chronic wasting diseases.
So much to say
If we are deficient in vitamin D
How to add it?
04
How to supplement vitamin D?
1. General measures: increase sunlight and intake of foods rich in vitamin D. Since there are few types of foods containing vitamin D, it is generally recommended to increase sunlight as the main supplement method. Methods of increasing sunlight: Expose the face and upper arms to sunlight for 5-30 minutes (depending on multiple factors) from 11:00 to 15:00 in spring, summer and autumn, 3 times a week to achieve the purpose of prevention. Vitamin D supplementation is recommended when there is a lack of sunlight.
2. Vitamin D supplementation for special populations such as pregnant and lactating women, children, osteoporosis, rickets/osteomalacia, chronic kidney disease-mineral and bone abnormalities should follow the recommendations of the appropriate specialists.
Source: Department of Endocrinology, Shenzhen Hospital, Guangzhou University of Traditional Chinese Medicine
Written by: Lai Xingrong