[Source: Qingdao Jiaozhou Central Hospital]
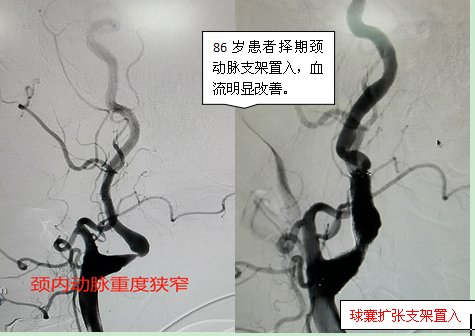
Recently, a 90-year-old man resisted the US and aided Korea VeteranSudden confusion, inability to speak, and physical disability, he came to the emergency department of Qingdao Jiaozhou Central Hospital for treatment. Emergency angiography showed carotid artery stenosis + middle cerebral artery embolism. , was given emergency carotid artery balloon-expandable stent placement, middle cerebral artery thrombectomy, and recovered to before the onset after surgery.
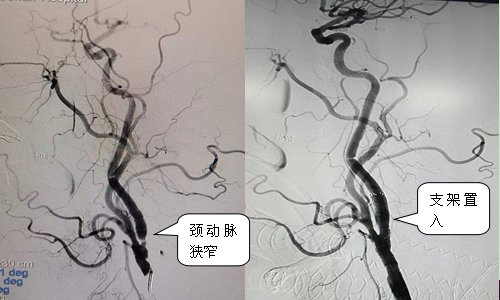
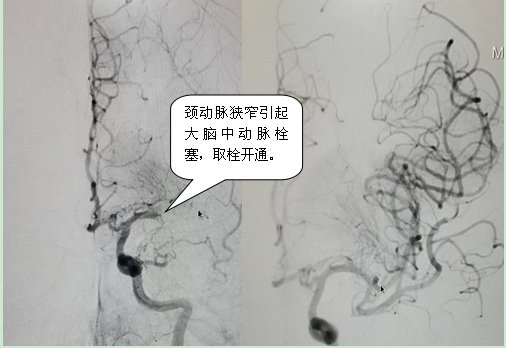
Carotid artery stenosis is mostly caused by atherosclerosis. Lumen stenosis/occlusion and plaque rupture and embolism can lead to ischemic stroke. According to literature reports, even with effective drug therapy, the incidence of cerebral ischemic events in patients with severe carotid stenosis is as high as2 within 26 years26 % or more; and 60% or more of cerebral infarctions are caused by carotid artery stenosis, and severe cerebral infarction can lead to disability or even death; As a minimally invasive interventional method for the treatment of carotid artery stenosis, carotid carotid angioplasty has achieved similar clinical results as traditional carotid endarterectomy, with the advantages of less trauma and quicker recovery. Carotid artery stenosis balloon angioplasty has now become a routine interventional procedure in our hospital.
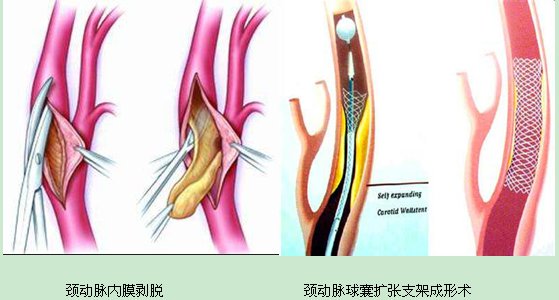
Carotid artery stenosis balloon dilatation and stent angioplasty indications
1. Symptomatic patient with nondisabling ischemic stroke or a Low-to-moderate surgical risk patients with transient cerebral ischemic symptoms (TIA, including cerebral hemispheric events or transient blackness) with ipsilateral internal carotid artery diameter stenosis greater than 50% by noninvasive imaging or angiography /span>.
2. Asymptomatic patients with ipsilateral internal carotid artery diameter stenosis greater than 70% detected by non-invasive imaging or angiography, expected perioperative period Stroke or mortality was less than 3%.
3. For patients whose neck anatomy is not conducive to CEA (carotid endarterectomy) surgery, CAS should be selected. span> (carotid stenting) without CEA.
4. For patients with TIA or minor stroke, if there is no contraindication to early revascularization, it can be done in the event of 2 span> weeks to intervene. For patients with large cerebral infarction with preserved partial neurological function, CAS treatment should be performed after at least 2 weeks of infarction.
5. Restenosis after CEA, symptomatic or asymptomatic stenosis greater than 70%.
6. CEA high-risk patients: older than 80 years old, with low cardiac output (EF less than >30%), untreated or poorly controlled arrhythmias, cardiac insufficiency; recent history of myocardial infarction, unstable angina: severe COPD; contralateral carotid occlusion, tandem lesions; Carotid artery dissection; pseudoaneurysm, etc.
7. Emergency patients, such as pseudoaneurysm, acute carotid dissection, traumatic carotid hemorrhage.
8. Carotid artery reconstruction is not recommended for severely disabled patients with cerebral infarction.
Carotid artery stenosis balloon dilatation stent angioplasty is a safe and effective solution for the treatment of carotid artery stenosis. . Carotid artery stenosis preoperative examination methods mainly include B ultrasound, CTA, MRA, DSA, etc. Inspection, early detection, early prevention, and early treatment can reduce the incidence of stroke and better benefit the general public.
Author: Ding Hongju
Editor: Song Xiaoling
Family Protection
Moisturize Life
Disclaimer: The copyright of this article belongs to the original author, if the source is wrong or infringes your legal rights , you can contact us by email, we will deal with it in time. Email address: [email protected]