“Why is a good blood sugar high? What are the complications of diabetes?”
Where there are doubts, there is Shendujun, today Deep Reading Jun will tell you the core secrets of diabetes.
“Diabetes Pathogenesis”, let’s go!
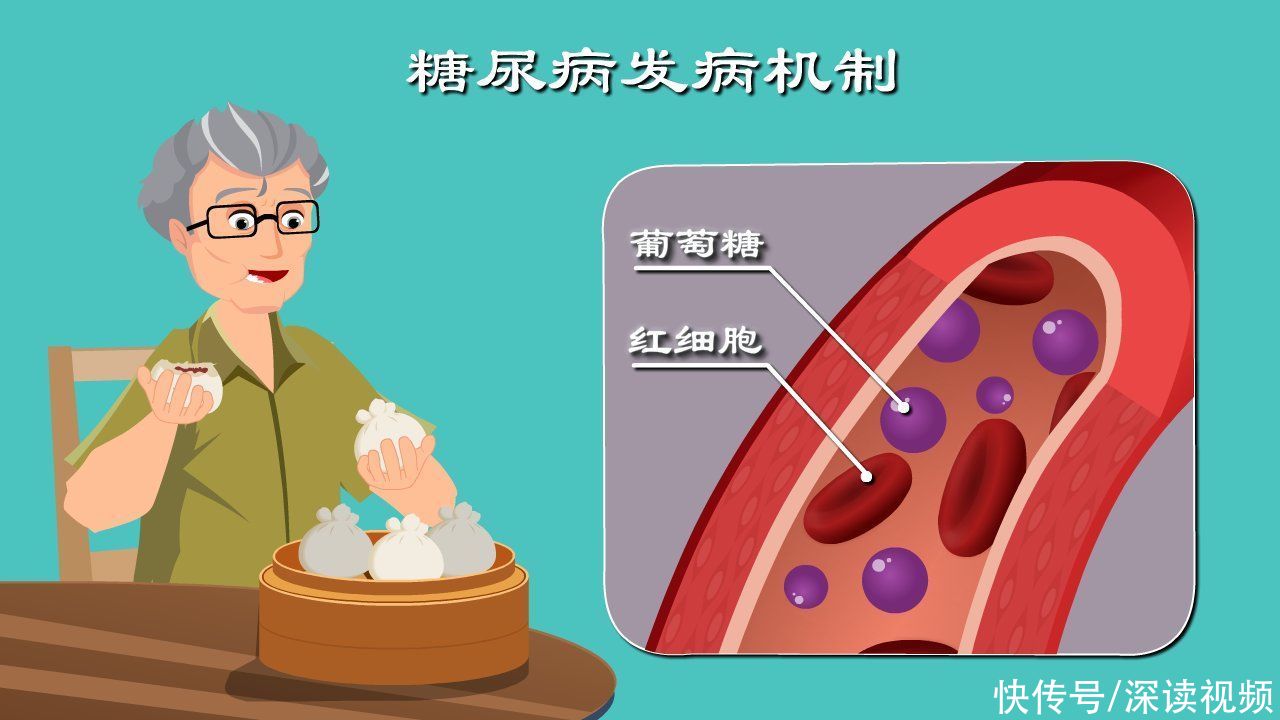
To learn about diabetes, start with blood sugar< /span>Start.
Rice and flour are starchy foods and belong to polysaccharides.
Starch is decomposed into maltose under the action of enzymes, which belongs to disaccharide.
maltose is decomposed into glucose under the action of enzymes, which belongs to monosaccharides, Common monosaccharides include fructose and galactose.
Only monosaccharides such as glucose and fructose can enter the bloodstream and become Glucose.
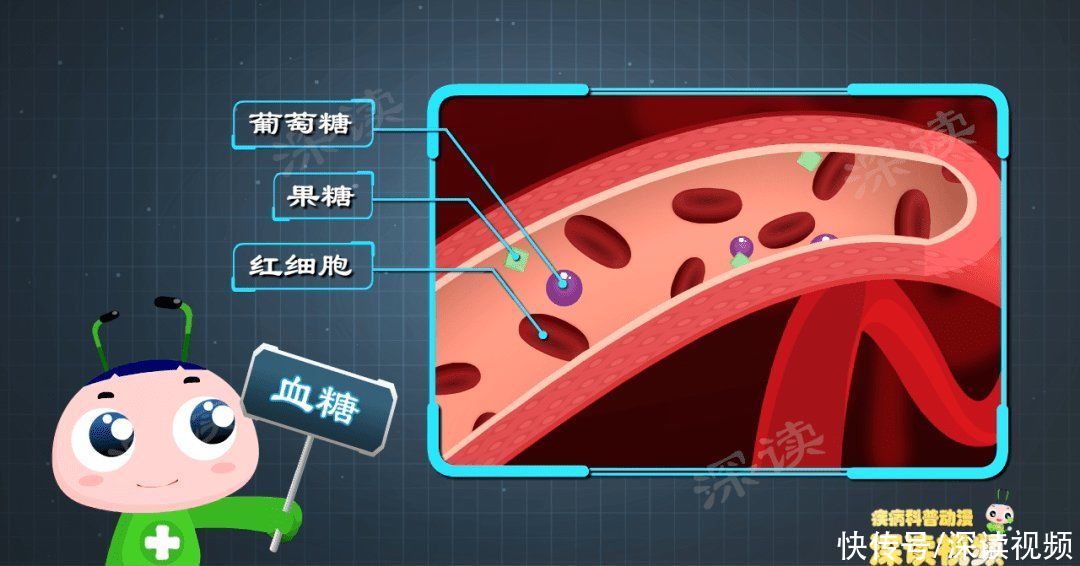
glucoseenter< /span>blood, blood is like a small train, taking sugar through the streets to various tissue cells .
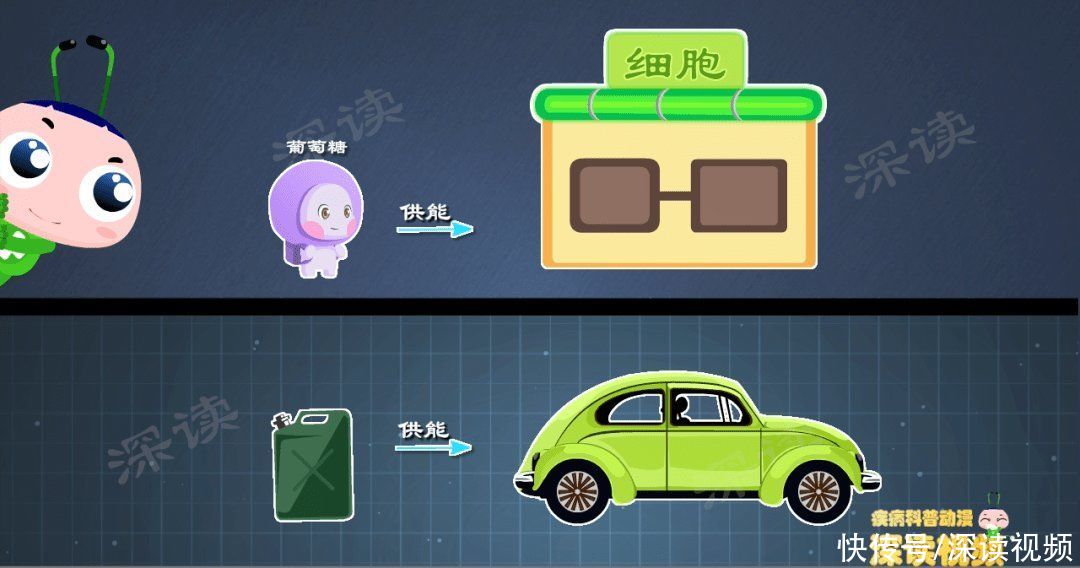
glucoseandcells< The relationship of span> is equivalent to the relationship between gasoline and automobile, glucoseiscell span>An important source of energy.
cellular metabolismrequires energy, work growth requires energy,sugar< /span>isthe energy source of cells. Only by eating sugar can cells survive, tissues and organs function normally, and people are healthy.
Deep reading, I will introduce you to a few big coffees who are closely related to blood sugar Bar.
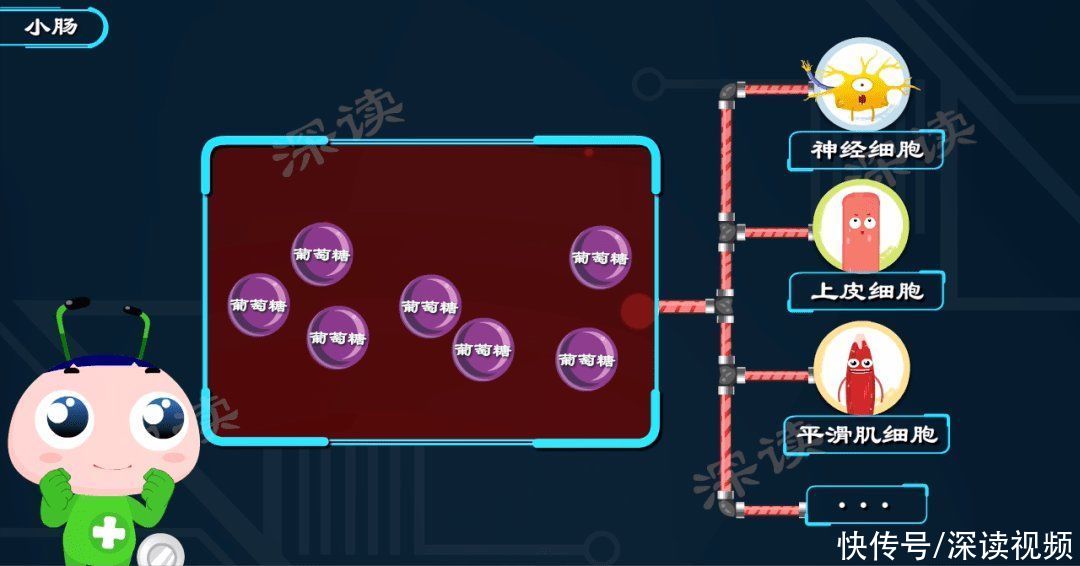
Small Intestine
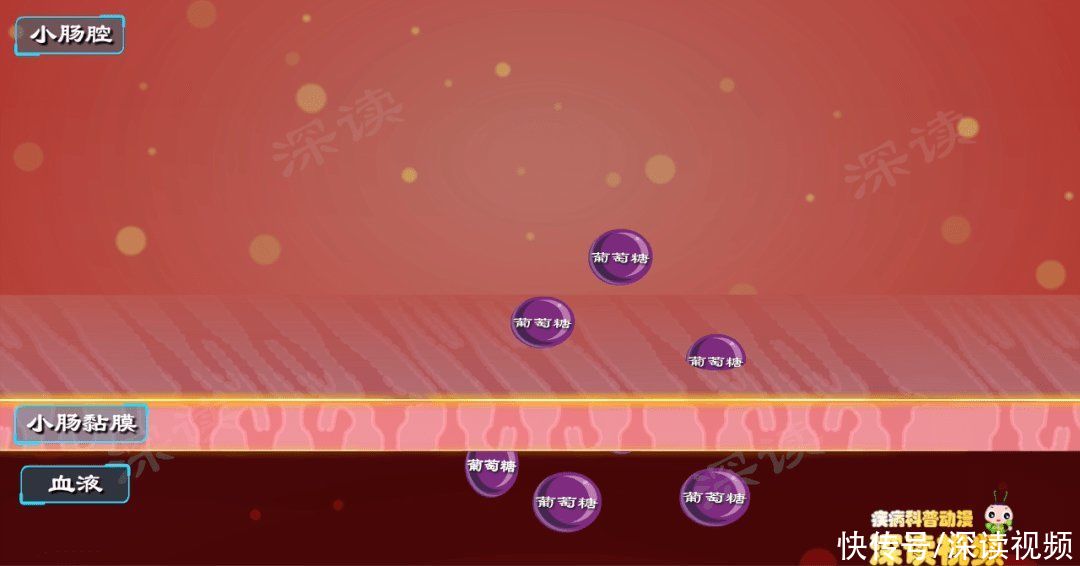
The Small Intestine isthe digestion of food and the main site of absorption, containing various Digestive juice, which can disassemble starches such as polysaccharidesinto< strong>Glucose. glucoseabsorbed into theblood, to Powers cells throughout the body.
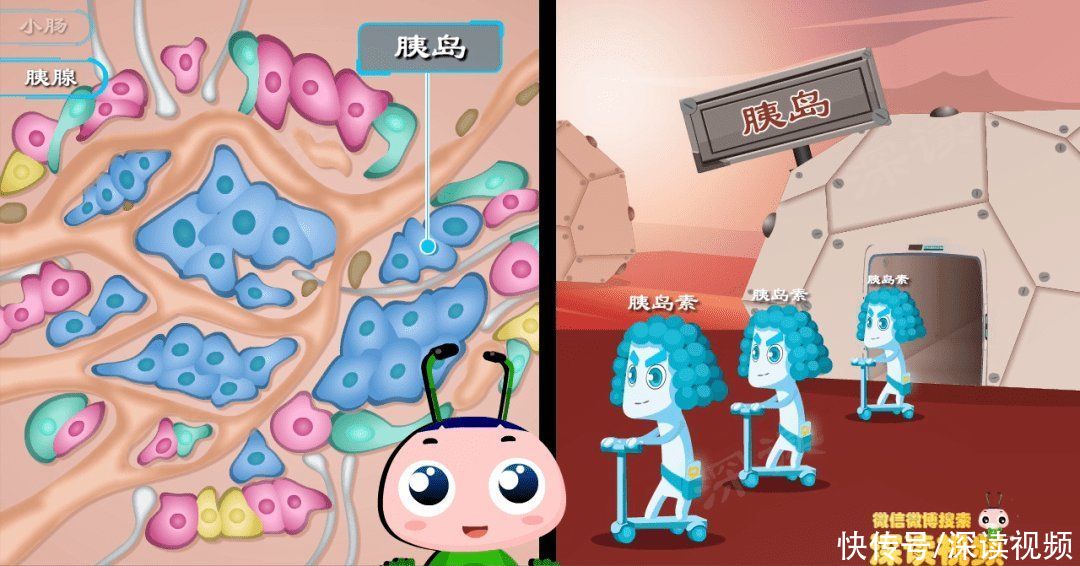
pancreas
< p>pancreasreclusivestomachbehind,The right side of the spleen, gray-red, soft, ten centimeters long, like a small sweet potato.
If you compare pancreas to a factory, then its two most powerful Such products are: digestive fluidsandspan>Insulin.
Zoom in, scattered inpancreas, these irregular cell populations are Islets, is the production workshop for insulin.
insulinis the only body in the body that can lower blood sugar ‘s hormone, glucoseto entercells , not withoutinsulin.

There is a layer outside the cellcell membrane, even if the sugar sticks to the cell’s face, it can’t eat the sugar directly.
cytoplasmthere is a special car called Glucose transporter.
insulinis just an errand, see the sugar coming, and rush to the cell home.
The cell family has a doorman who specializes in receivinginsulininformation, medically called insulin receptor.
Uncle the guard received the message and knew that there was sugar coming to the door, so he quickly arranged a sugar car to pick up the sugar at the designated location, and the sugar entered the cells like this.
Withoutinsulin, cells don’t know that sugar is coming, and sugar starts at the root lost access to cells.

How the small intestine and pancreas work together?
The moment glucose passes through the small intestine to blood sugar, small intestinal epithelial cells< span>A hormone called glucagon-like peptide-1 is produced.
This product is responsible for notifyingpancreas: “Don’t sleep! Get up and secrete insulin Hey!”, so pancreasbegan to secreteinsulin< span>.
insulinon the blood train, ran to the door of each cell and informed the cell’s guard, ” Here comes the sugar! Here comes the sugar!”.
Therefore, the cells prepare their own special car to pick up sugar, pick up blood sugarEntercell.

Read the summary of Jun Xiao:
“Four buns, a bowl of tofu brain.”
small intestine During the digestion of food, glucosepasses through the small intestine into the bloodstream,blood sugar strong>The content keeps rising.
insulinnotifies cells,cellsDrag the glucose home, with the progress of this series of actions, the content of blood sugar also changes from high to low, slowly Slowly returned to the pre-dinner level.
During this process, you are full, and cells are also full . blood glucose experienced a peak, a fall, and returned to normal within 2 hours. Like nothing ever happened.
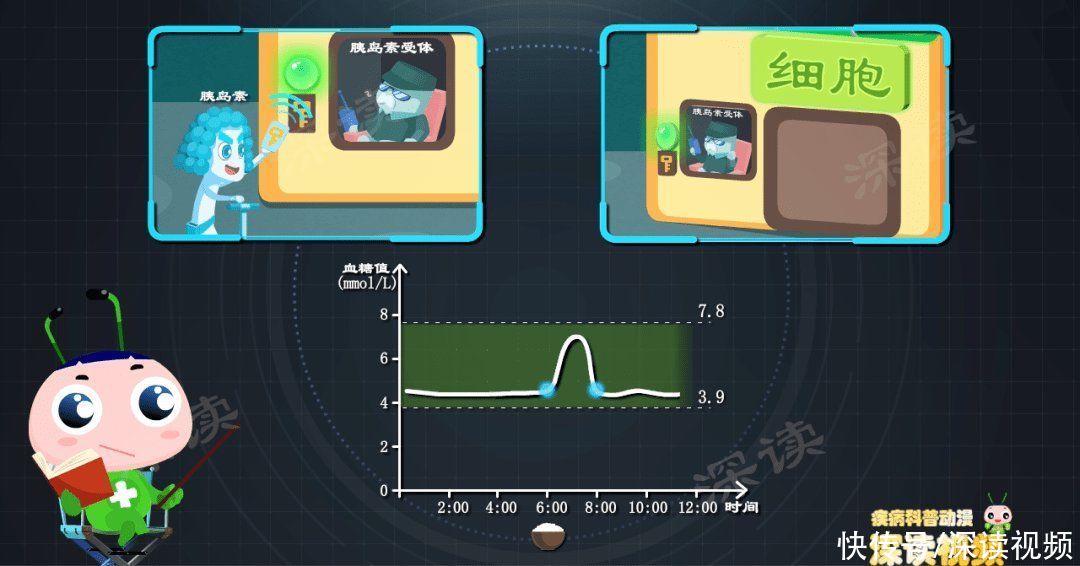
During the process of blood glucose metabolism, the casts played include: small intestine, pancreas, glucagon-like peptide-1, insulin , insulin receptors, glucose transportersand more.
These casts worked perfectly together to put on a show that made glucose< span>It is metabolized smoothly in the body.

Then the question is, what does the big show of glucose metabolism in diabetic patients look like?
After the blood sugar is high, what kind of torture are the blood vessels suffering? Are your heart, liver, and kidneys all right?
The next episode “Interpretation of Diabetes Symptoms”, Deep Reading will reproduce the disaster scene of high sugar for you!
Follow “Deep Reading Video”, remember to like and forward! mwah!