內容目錄
In recent years
thyroid nodulesbecome after the “three highs”
span>
The second most frequent visitor on the medical report

Relevant physical examination data show
in Chinese adults
thyroid nodulesThe incidence rate is about 20%~76%
equivalent to 1 in 5 people
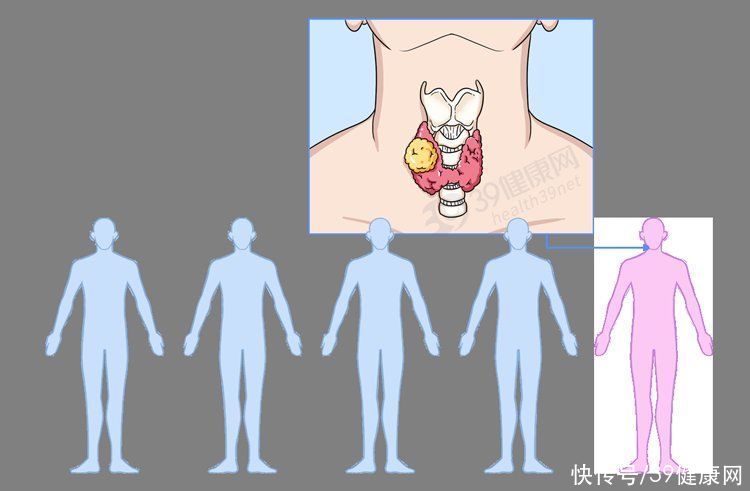
Many people hear “nodule”
Many questions arise:
Can thyroid nodules become cancerous?
How to distinguish benign from malignant?
Do I need surgery?
…
Don’t panic
Today, Uncle Jiu will talk about
several important questions about thyroid nodules
01 Why Thyroid nodules
nodules
speaking bluntly, it is a pile of proliferative masses
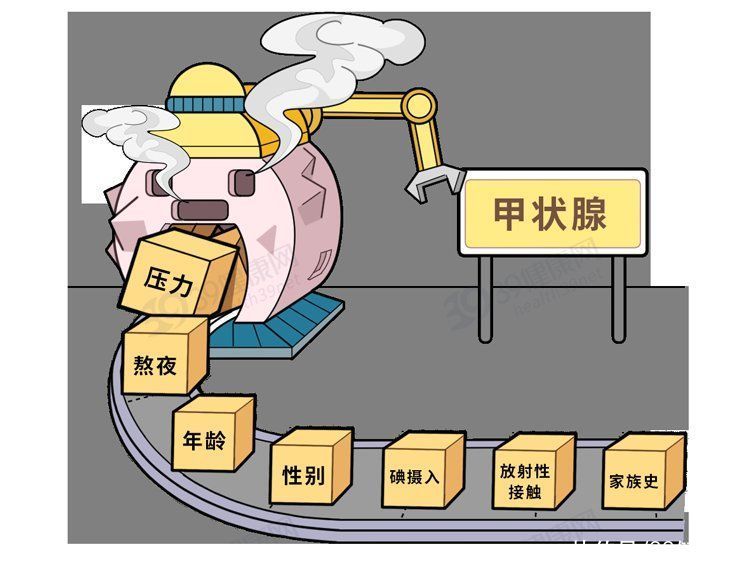
The reasons for stimulating thyroid nodules
are roughly as follows:
- < span>Long-term emotional anxiety and stress;
- iodine deficiency or excessive intake;
- familial inheritance;
< li>Exposure to radioactive material;
ul>
02 What should I do after a nodule is found?
There are benign and malignant nodules
different nature
diagnosis and treatment plan Also different
pass routine4 thyroid tests
Basically you can judge the quality of the nodule
①palpation:
< p>Preliminary judgment on whether there are nodules
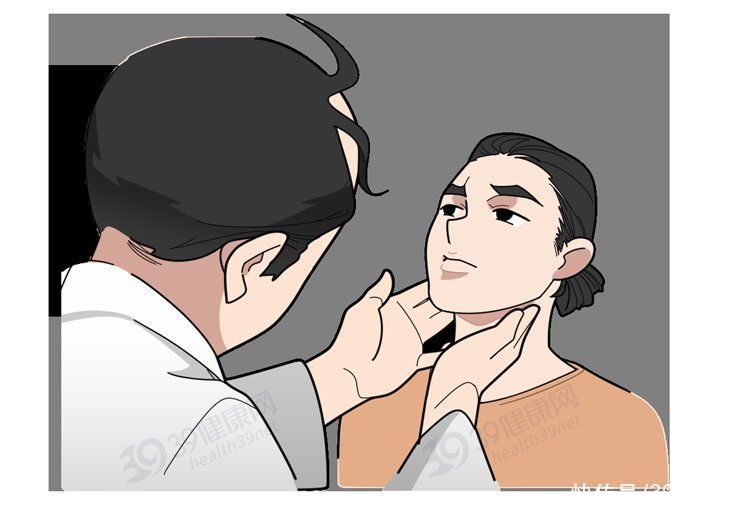
The doctor passed the neck examination< /span>
Preliminary assessment of nodules
②blood test< span>:
Assess for normal thyroid function
Cannot diagnose whether the nodule is benign or malignant p>

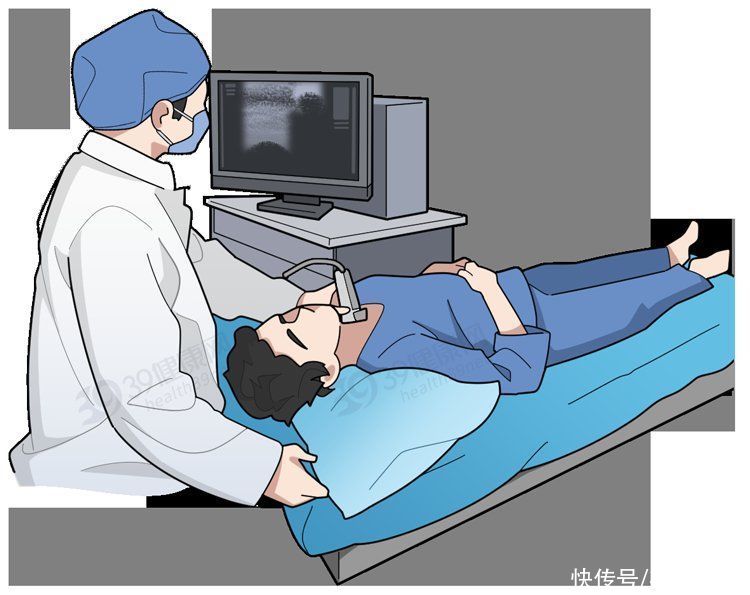
③Thyroid Ultrasound:
< span>Preliminary judgment on the nature, size and number of nodules
on the ultrasound diagnosis reportTI-RADS classification
Good review assessing the safety of thyroid nodules

if nodule levelGrade 4 and above
recommendedneedle biopsy< /strong>Come onStep by step to determine
whether it is a malignant nodule
in addition
Pay special attention if the following “words” appear on the report

④Puncture biopsy:
Determine the quality of the nodule
< p>Tissue specimens drawn by fine needle aspiration
cellspathological examination< /p>
Can effectively distinguish benign from malignant thyroid nodules
reduce unnecessary surgery
The entire puncture operation
only takes a few minutes to complete
no noticeable Trauma
in clinical data
< strong>Less than 5% of nodules
probability of developing thyroid cancer
The remaining 95% are benign
even if diagnosed with thyroid cancer< /span>
The death rate is also lower
only 0.076/100000
As long as timely treatment, most of the disease can be controlled
03 If there is a nodule, is surgery necessary?
If it is found in the early stage Small nodules
can be treated without surgery
but needevery 3 ~6 months
Regularly check thyroid hormone levels, B-ultrasound
if benign nodules continue to increase Large
more than 4cm in diameter
with pressure, hoarseness, and difficulty swallowing Situation
or malignant nodules are found
surgery should be considered
In addition
If the thyroid function is abnormal< /span>
also needs treatment
Take hyperthyroidism as an example
needs Taking antithyroid drugs
combined with radioactive iodine therapy or surgery
relief and control the disease
04 How to prevent and control?
①Regular check-ups are required
healthy adults
EspeciallyAdult women over 35 years old
It is recommended to have a thyroid function test every 5 years and B-ultrasound
Persons with a history of thyroid nodules
thyroid examination at least once a year

②Stay optimistic and positive
< span>The state of the immune system
is directly linked to the health of the thyroid
When a person is long-term
When you are in negative emotions such as anxiety and depression
it is easy to cause immune dysfunction
finally Involves the thyroid
so
Less anxiety and learn to relieve stress
Necessary

③Keep away from radiation
Ionizing radiation is associated with thyroid nodule formation
and cancerous Important incentives for birth
Therefore
try to stay away from your life as much as possible
reduce possible radiation exposure

④Control the iodine intake in the diet
Insufficient or excessive iodine intake
can cause nodules
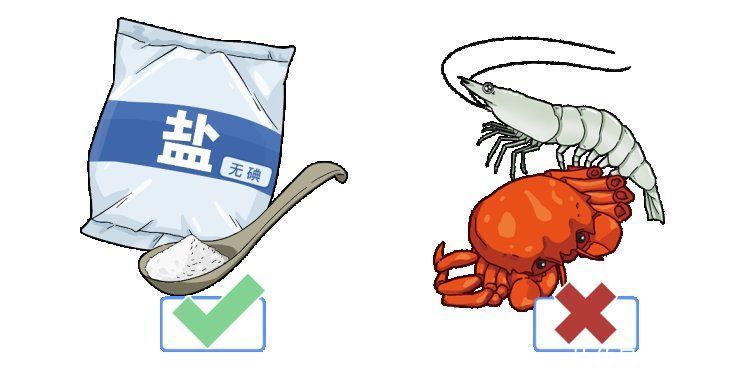
thyroid nodules associated with HyperthyroidismPatients
should choose non-iodized salt
And reduce seafood
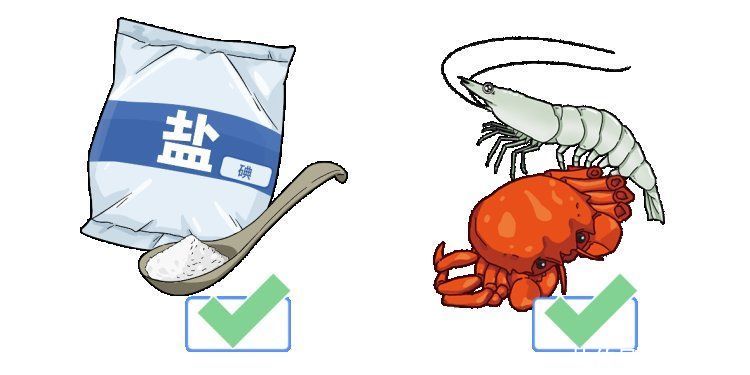
thyroid nodule with < /span>hypothyroidismpatients
iodized salt is optional
It is recommended to consume Shanghai products more than 2 times a week
such as fish and shrimp, shellfish, seaweed and kelp
Overall
A thyroid nodule on physical examination is nothing Major event
Regular review and cooperation with treatment
can better control the disease
< p># Yao Zero Zero Plan#
References:
[1] Liu Mao. Wang Peihua. Analysis of influencing factors of thyroid nodules. [J] Jiangsu Preventive Medicine , 2017, 28(6)
[2] Yang Tao. Don’t be careful with thyroid nodules, 95% are benign. [N]Modern Express, 2020-6-30
[3] Zhou Qinghua, Fan Yaguang, Wang Ying, et al. Guidelines for Classification, Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Nodules in China (2016 Edition) [J]. China Journal of Lung Cancer, 2016, 19(12): 793-798.
[4]Rong Xueyu. Ji Hongtao. Preliminary application of three-dimensional ultrasound in the differential diagnosis of benign and malignant breast nodules.[N]. 2008(024), 008
[5]Kaliszewski et al. “American Thyroid Association Management Guidelines for Adult Patients with Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer: The American Thyroid Association Guidelines Task Force on Thyroid Nodules and Differentiated Thyroid Cancer.” (2017).
[6]Cooper, David S et al. “Revised American Thyroid Association management guidelines for patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer.” Thyroid: official journal of the American Thyroid Association 19 11 (2009): 1167-214 .
[7 ]Stavros, Athanasiou et al. “Solid breast nod ules: use of sonography to distinguish between benign and malignant lesions.” Radiology 196 1 (1995): 123-34.